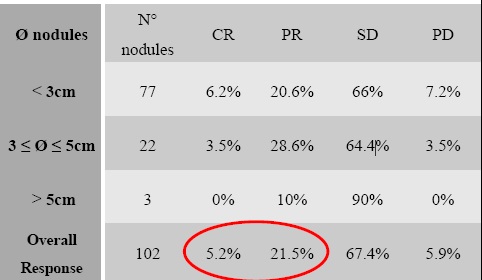
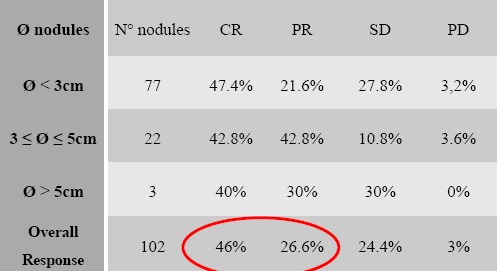
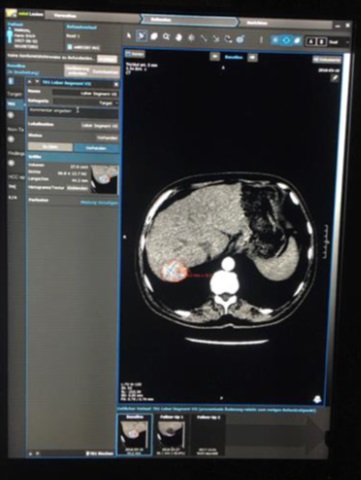
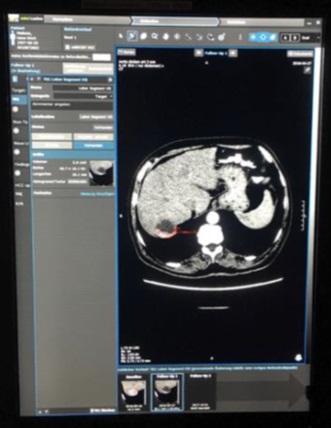
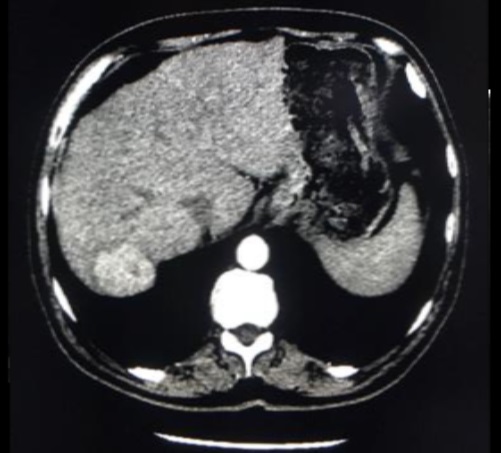
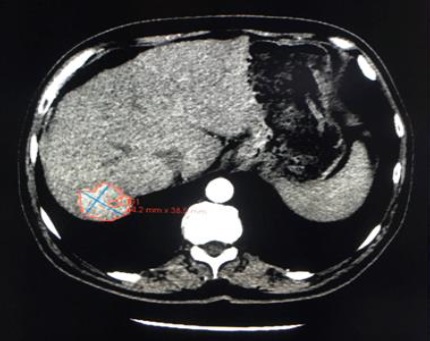
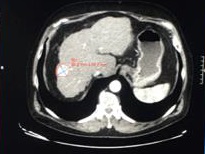
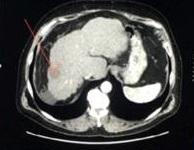
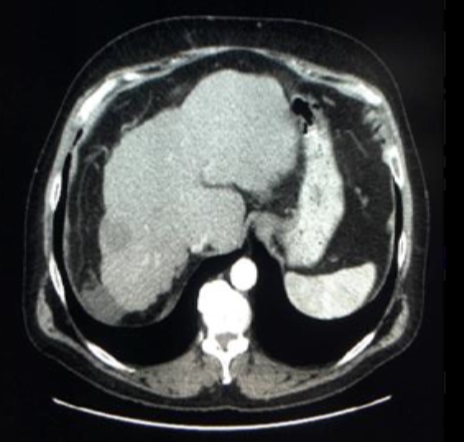
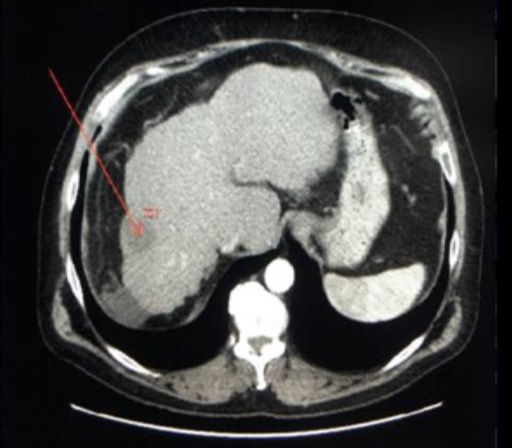
一组小粒径DEB-TACE的报告(102个结节,结果1)
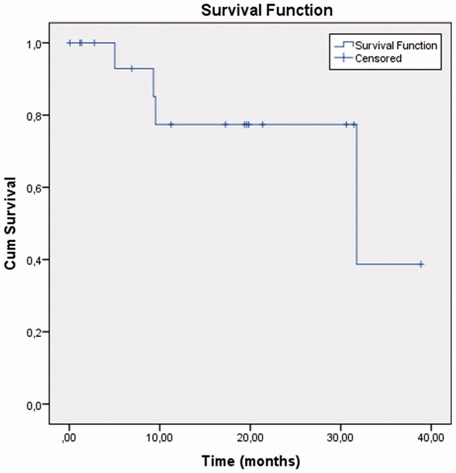
Mean Follow Up Period: 357 days (30-810)
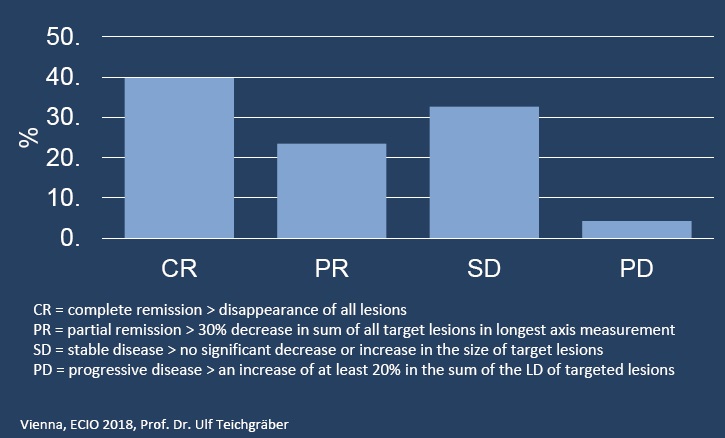
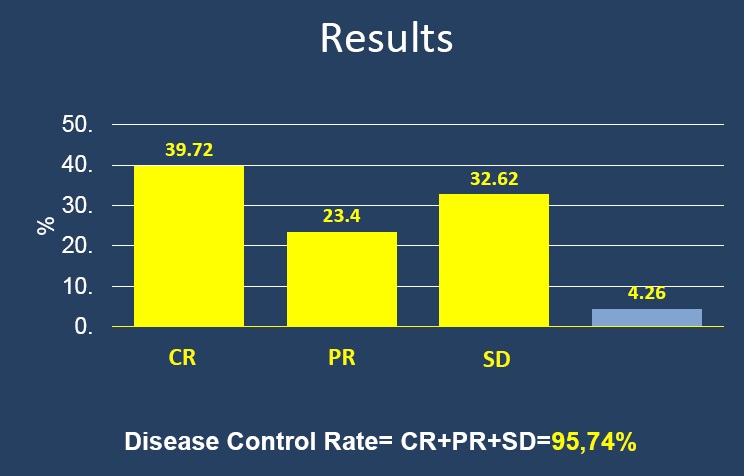
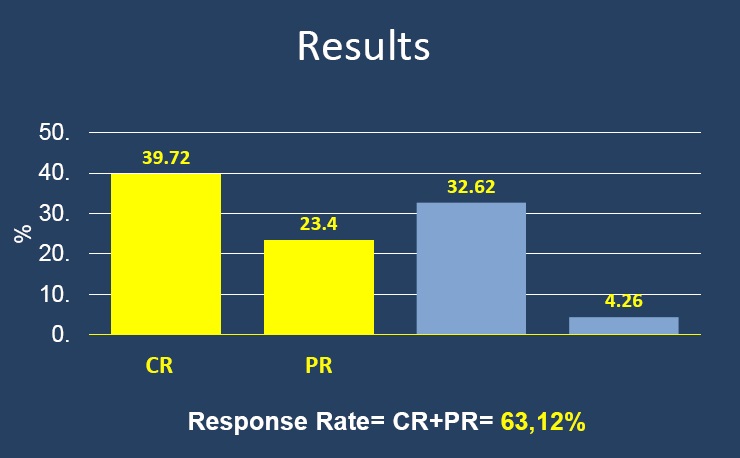
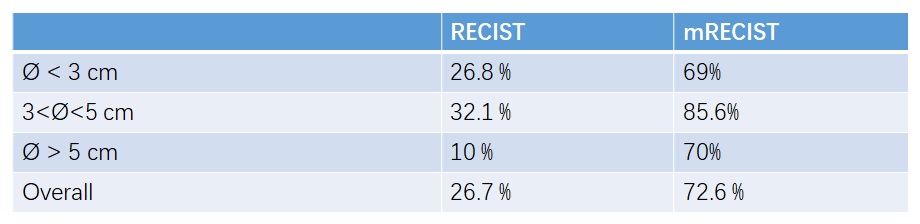
以客观有效率,两种判定肿瘤治疗客观有效率的方法都是有效的,结节越小完全坏死率越高
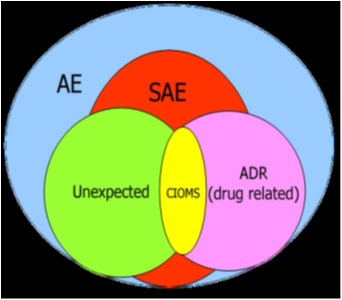
Objective Response( CR+ PR )
 小粒径栓塞(结果2)
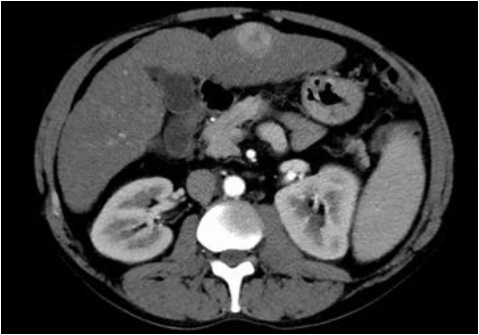
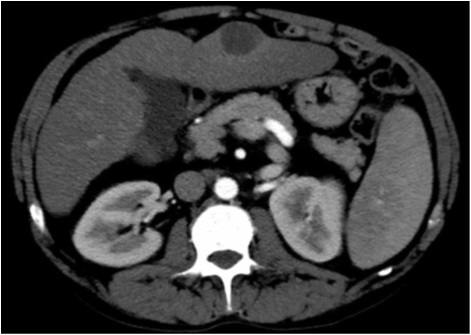
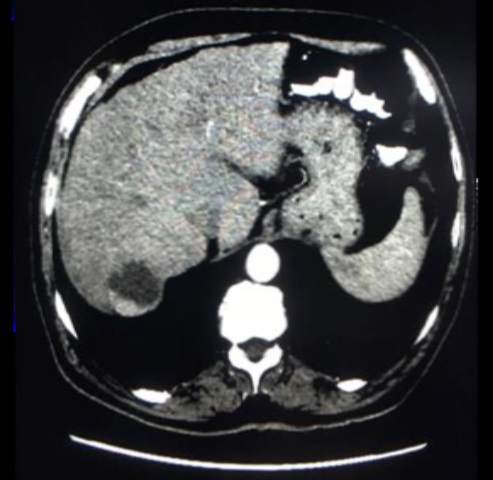
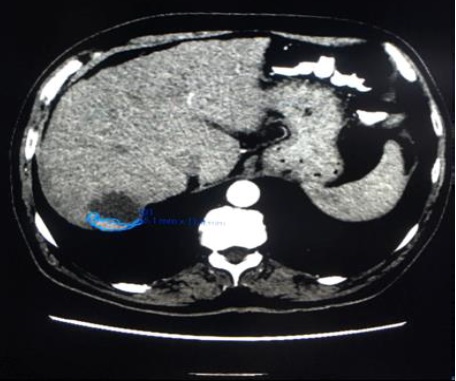
Arterial phase CT scan of 32mm HCC nodule in segment III, before and after 1 cycle of DEB TACE with 40 um particle. CR according to mRECIST and SD according to RECIST
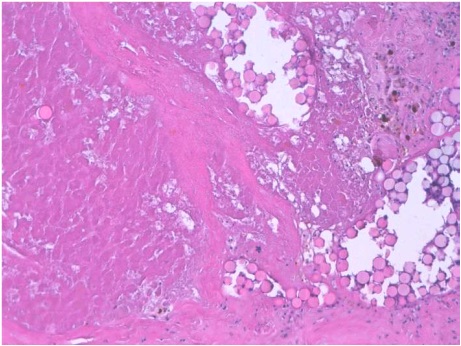
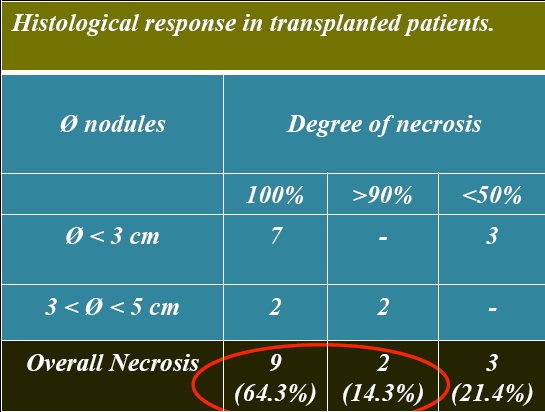
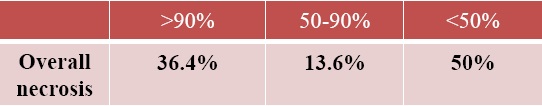
证据:小粒径DEB-TACE肝移植后的结果【8】
- 11/48 patients received OLT
- Medium time before OLT: 4.8 months
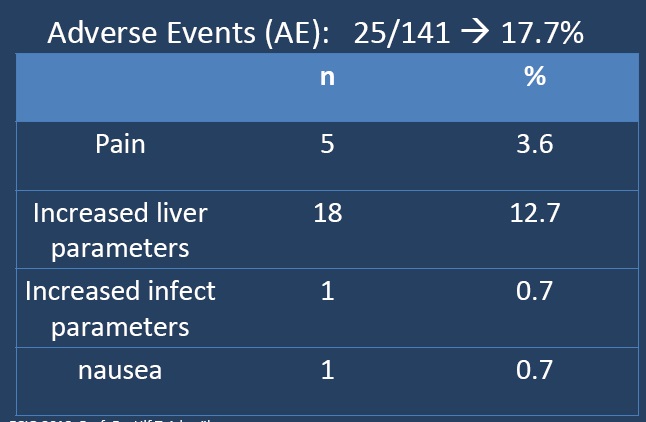
小粒径DEB-TACE的副作用 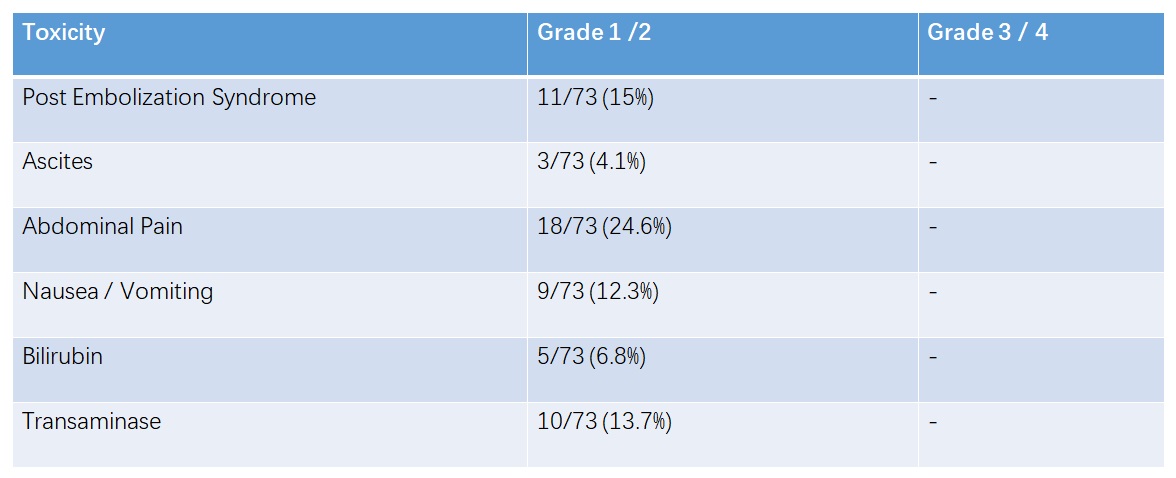
Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) 4.0
结论:
Initial study results of DEB TACE with 40μm particles show efficacy and a positive safety profile for the treatment of early-intermediate HCC.(早期研究安全有效)
Objective Response, local disease control and adverse events rate in this study is better than reported in literature with bigger particles (100-300 μm) and comparable to recent studies made using particles with similar diameters (30-60 and 70-150 μm)(小粒径比大粒径好)
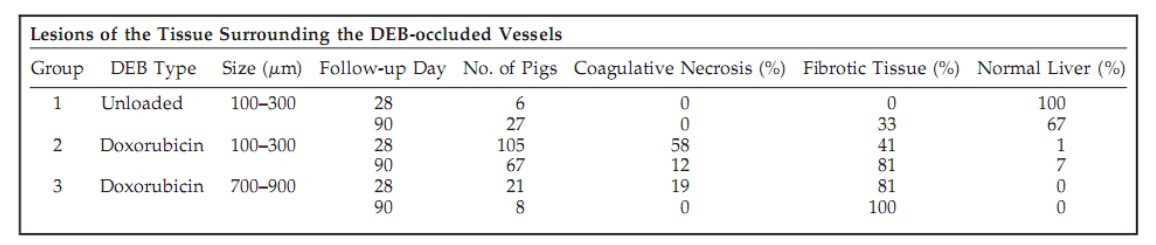
Histological necrosis rate in transplanted patients was satisfying in nodules with diameter below 3 cm and less satisfying in bigger nodules. 肝移植组织学完全坏死<3cm结节比大结节好
Superselectivity and tight calibration resulted in less local and systemic toxicity. (超选择)
Further studies with bigger sample of patients and control group are needed to confirm initial results(还需要大样本对照组研究)
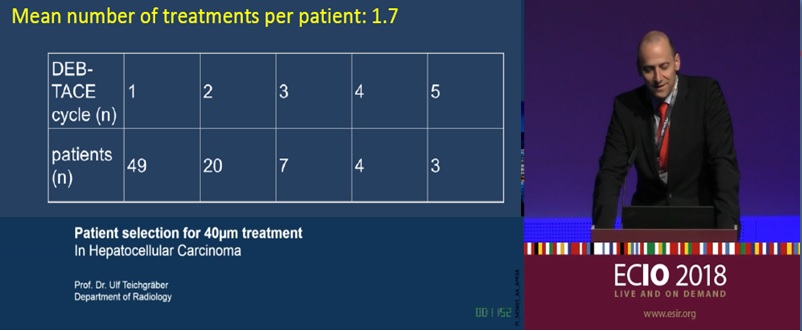
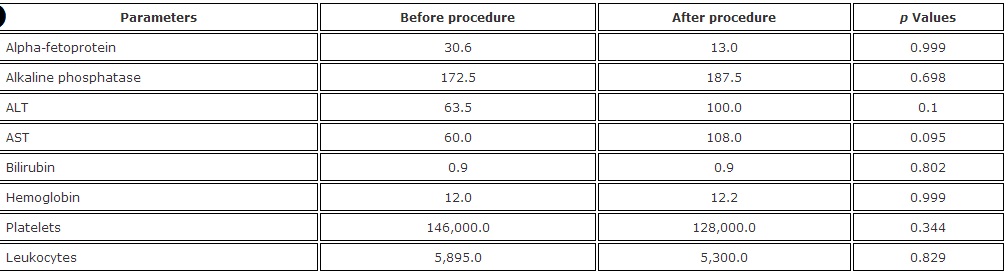
There was no statistically significant influence on these parameters; however, due to the small size of the sample, an effect cannot be ruled out. The median differences in biochemical parameters between the pre- and post-treatment time points are listed in Table 5
DEB-TACE:Is Drug Delivery the Main Aim?
Chemo- or Bland-embolization??
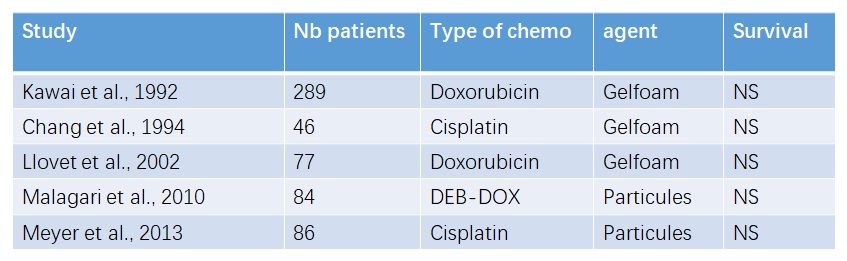
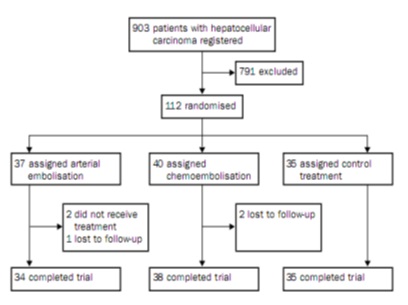
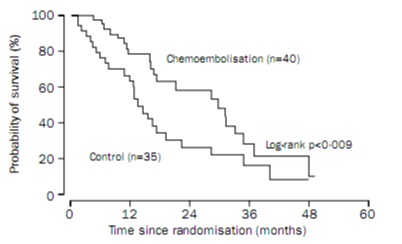
Superiority of chemoembolization : No proof!
5 negative randomized trials…
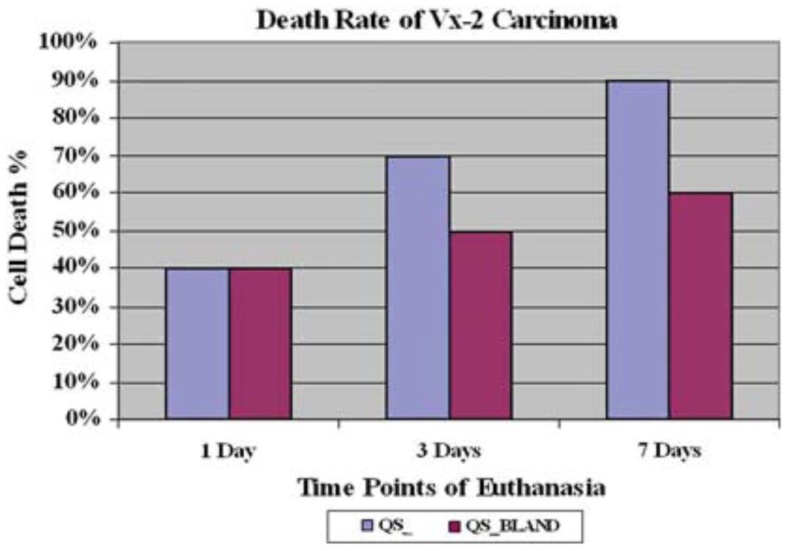
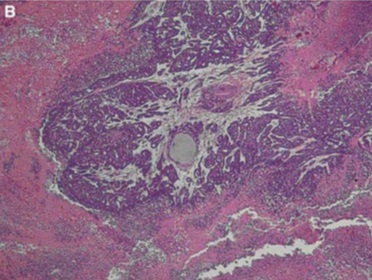
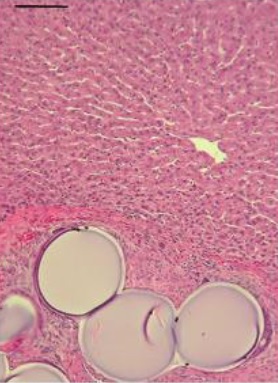
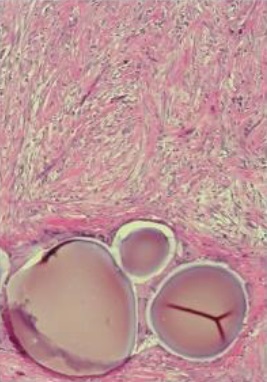
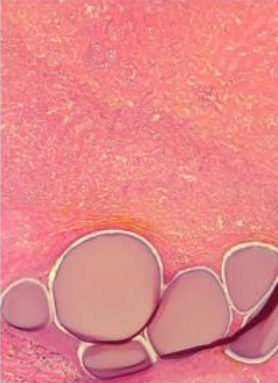
试验动物病理证实:化疗药物有效
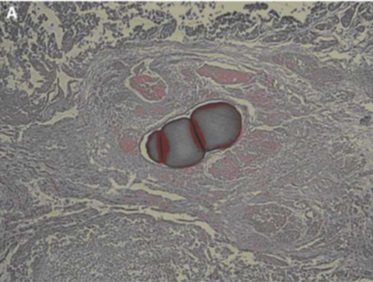
Persistance of viable tumor with bland embolization
Lee, CVIR 2010
1. Kan Z, Madoff DC .Liver anatomy: microcirculation of the liver. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2008 Jun;25(2):77-85
2. Idée JM, Guiu B. Use of Lipiodol as a drug-delivery system for transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma: a review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013 Dec;88(3):530-49
3. Zhou X et al. Doxorubicin-eluting beads versus conventional transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014 Nov 15;7(11):3892-903 4. Xie ZB et al.(2015) Systematic review comparing the safety and efficacy of conventional and drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res 45(2): 190-200 5. Bonomo G et al (2010) . Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 33:552–559 6. Ruben Lopez-Benitez et al (2009). Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32:615–622 7. Lammer J et al. Precision V. (2010) Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 33: 41-52 8. Nicolini D, et al.Doxorubicin-eluting bead vs conventional transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma before liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Sep 14;19(34):5622-32 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||