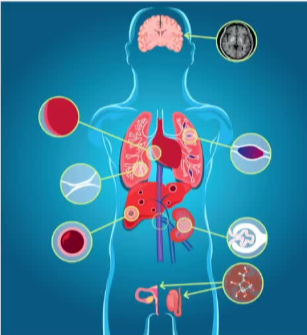
先天性门静脉-体循环分流 - 先前称为Abernethy畸形,也有称先天性门静脉发育不全 - 胚胎起源: - 1:30,000 ~ 50,000活产婴儿 - 在其他哺乳动物中也有此类表现 - 人类:诊断延迟直到→严重症状 没有通用的命名法→ 功能性命名【Franchi - Abella 2018】 国际上有一个 International Registry of Congenital Portosystemic Shunt members 先天性肝门静脉系统分流(CPSS)是一种罕见的血管畸形,它建立了肝门静脉和体循环静脉之间的异常连接,导致肝门静脉血流完全或部分从肝脏转向体循环静脉系统。 存在不同的解剖类型,并提出了几种分类方法。它们可能与其他畸形有关,特别是心脏畸形和异位。主要并发症包括肝性脑病、肝癌、肝肺高压和肺动-静脉分流。诊断依赖于影像学,产前诊断也是可能的。在生命的第一年,某些解剖形式的CPSS可能会自发闭合。当CPSS仍然开放时,放射学或外科手术闭合CPSS可以预防、解决或稳定并发症。介入放射学在术前评估中发挥关键作用,通过栓塞试验评估确切的解剖结构并在CPSS栓塞后测量肝门静脉压力。当可能时,内血管闭合是治疗的首选方案。
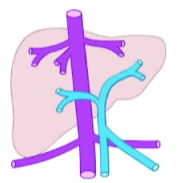
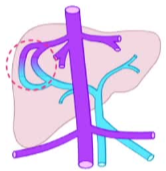
定义/命名法-肝内和门静脉主干表现
|
 |
 |
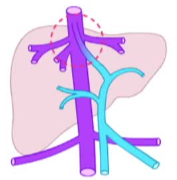 |
| 正常 | 门静脉-肝静脉分流 | 静脉导管未闭 patent ductus venous |
【Guerin F 2020 Franchi - Abella 2018】
【Guerin F 2020 Franchi - Abella 2018】
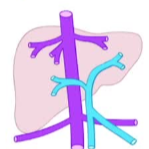
定义:命名法-肝外
主要门静脉存在,肝内门静脉根小或无 main portal vein present ,intrhepatic portal radicles small 或absent
 |
 |
 |
| 正常 |
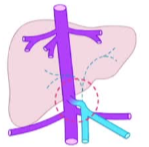
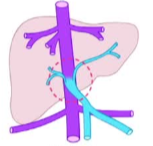
端到侧伴或不伴异位门静脉
|
左右 side to side
|
损害肝的第一次滤过,导致 → 体征和症状
产前(prenatal)
出生后婴儿(post natal)
成人(adult)
CPSS(congenital portosystemic shunts) 多系统疾病
分流不太可能自动关闭
伴有最严重的体征和症状
介入医生的角色,寻找门静脉的证据(闭塞试验)
介入医生的角色,寻找门静脉的证据(闭塞试验)
诊断
在无症状患者中偶然发现。
产前(prenatal)
出生后婴儿(post natal)
成人(adult)
在症状性患者中表现各异(wide clinical spectrum)
CPSS(congenital portosystemic shunts) 多系统疾病
症状性-肝
结节性肝 Nodular liver
- 再生增生 Nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- 局灶性结节性增生Focal nodular hyperplasia
- 腺瘤Adenoma
- 肝母细胞瘤Hepatoblastoma
- 肝细胞癌Hepatocellular carcinoma
- 血管瘤Hemangioma
脂肪变性Steatosis
左肝增生不良Hypoplastic left liver
组织学和分子异质性
生化
-- LFTs正常 Normal LFTs
- 胆汁淤积-Cholestasis
- 血浆胆汁酸升高Elevated plasma bile acids
- ↑半乳糖-1-磷酸↑ galactose-1-phosphate
- ↑血浆NH4*↑ plasma NH4*
症状性-心肺
|
肝肺综合征 hepatopulmonary syndrome 肺动脉高压 pulmonary hypertension 高输出量心力衰竭 high output heart feilure |
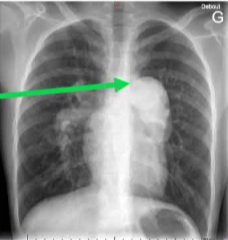 |
| 肺动脉高压 |
症状性-脑
|
轻微的认知缺陷Subtle cognitive deficits
无法解释的智力低下Unexplained mental retardation 餐后意识丧失Post-prandial loss-of-consciousne 帕金森样Parkinson-like 肝性脊髓病Hepatic myelopathy 锥体系统缺陷,Pyramidal deficits |
 |
神经认知表现多样性 【Chabbey L 2024 Spahr 1999 Hanquinet 2017】
症状性-内分泌
|
Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia高胰岛素低血糖
Hyperandrogenism 高雄激素症 Amenorrhea 更年期 Precicious puberty青春期 Hypothyroidism 甲状腺功能减退 Fertility? 生育能力?
、、、、、
|
 |
| 【Bahadori A 2022 Chocarro 2016】 |
症状性 = 肾 kidney
蛋白尿
血尿
【Bernard 2012 Karashima 2000 】
CPSS congenital portosystemic shunts 先天性门静脉-腔静脉分流是一个多系统疾病【 BERNARD S 2012】
 |
 |
症状相关疾病,
CPSS可能被误诊,或没有充分诊断
| Caroli's | Noonan |
| Goldhenhar | Cornelia de Lange |
| Down's | Holt-Oram |
| Turner | Costello |
| Leopard | Wolf-Hirschhorn |
| Rendu-Osler | Neurofibromatosis |
| Grazioli | Adams-Oliver |
推荐检查:
Head to toe assessment Recommended work-up 【Sokollik C 2013】
- 腹部US +多普勒Abdominal US + Doppler
- CT血管造影→门静脉造影CT angiography→portal venogram
- 寻找其他畸形Look for other malformations
- 心脏造影剂超声Cardiac contrast echo
=检查压力异常If pressures abnormal
-右心导管检查Right heart catheterization
- 肺扫描(HPS)Lung scan (HPS)
- 脑MRI及行为评估Brain MRI & behavioral assessment
- 肝活检Liver biopsy—潜在的肝脏疾病?如果结节?underlying liver disease? Nodules?
- 脑MRI及行为评估Brain MRI & behavioral assessment
- 肝活检Liver biopsy—潜在的肝脏疾病?如果结节?underlying liver disease? Nodules?
- 肝脏生化,凝血,胆汁酸,NH4-Liver biochemistry, coagulation, bile acids, NH4
一个基本原则:
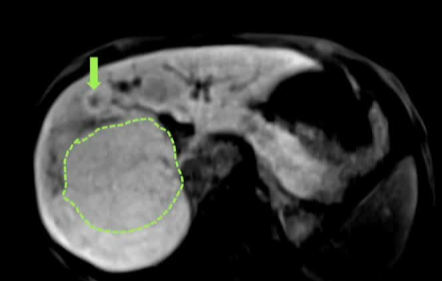
在有肝结节但无潜在肝脏疾病的年轻患者中寻找CPSS,Look for CPSS in young patients with a liver nodule and no underlying liver diseaseI
已知CPSS的患者寻找肝结节并确定其特征 In patients with known CPSS look for liver nodules and characterize them
在有肝结节但无潜在肝脏疾病的年轻患者中寻找CPSS,Look for CPSS in young patients with a liver nodule and no underlying liver diseaseI
Patients with CPSS have a high cumulative prevalence of liver masses, reaching 73% CPSS患者肝脏肿块的累积患病率高,可达73%

如何正确管理CPSS?How to properly manage CPSS?
一、肝结节的放射学评估。Cross-sectional radiological assessment of thel iver nodules 【】
1. 在肝结节闭合前后,仔细评估和终身监测是必不可少的A careful evaluation and lifelong surveillance of liver nodules is essential, before and after closure
2. 大多数肝结节为良性(FNH和HCA),且往往发生在较年轻的年龄。Most liver nodules are benign (FNH and HCA), and tend to occur at a younger age
3. CPSS儿童中有HCC和HB的报道,大小似乎从良性FNH和NRH逐渐增加,到HCA和HCC HCC and HB have been described in children with CPSS,Size seems to increase progressively from benign FNH and NRH, to HCA and HCC
4. CE-MRI和CEUS是结节成像的首选方法。CE-MRI and CEUS are the preferred methods to image nodules.
3. CPSS儿童中有HCC和HB的报道,大小似乎从良性FNH和NRH逐渐增加,到HCA和HCC HCC and HB have been described in children with CPSS,Size seems to increase progressively from benign FNH and NRH, to HCA and HCC
4. CE-MRI和CEUS是结节成像的首选方法。CE-MRI and CEUS are the preferred methods to image nodules.
- 使用肝胆造影剂的MRI对基线评估是必要的。MRI with hepatobiliary contrast agents is essential for baseline evaluation
- 使用细胞外造影剂的MRI可以进行纵向成像 Longitudinal imaging can be performed using MRI with extracellular contrast agents
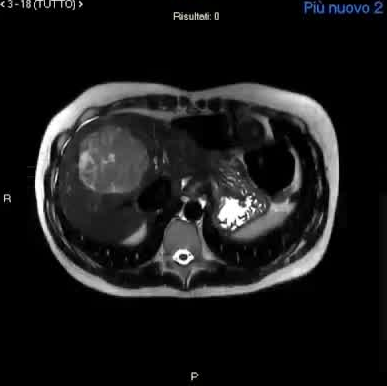
CPSS-Nodule characterization
β-catenin activeated hepatocellular adenoma
- 使用细胞外造影剂的MRI可以进行纵向成像 Longitudinal imaging can be performed using MRI with extracellular contrast agents
CPSS-Nodule characterization
 |
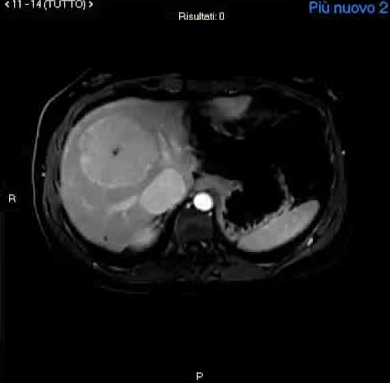 |
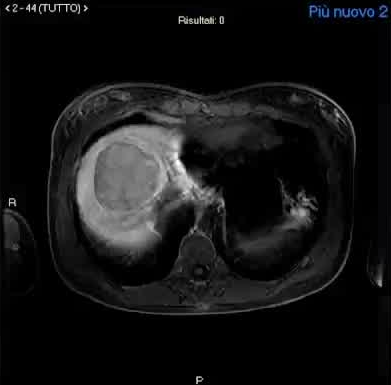 |
二、 闭塞试验计划分流闭合 Occlusion test to plan shunt closure
CPSS - Occlusion TEST
仔细的术前评估是必要的:A careful pre-operative assessment is essential:
1. 了解确切的分流解剖、压力和流量;To understand exact shunt anatomy, pressures, and flow
1. 了解确切的分流解剖、压力和流量;To understand exact shunt anatomy, pressures, and flow
2. 在分流关闭前检测肝外并发症;To detect extrahepatic complications prior to shunt closure
3. 减轻手术风险和门脉高压风险;To mitigate procedural risks and the risk of portal hypertension
CPSS anatomy is extremely variable and complex, and it is best assessed using Color Doppler ultrasound, CT-angiography and MRangiography or a combination of these techniques
CPPS 解剖非常多变和复杂,最好使用彩色多普勒超声、ct血管造影和MRangiography或这些技术的组合进行评估
三、肝结节活检。Liver nodules biopsy
1. 当对结节进行活检时,也要对非结节性肝脏进行活检,以排除原发性肝脏疾病。When performing biopsy of a nodule, also obtain biopsy of the nonnodular liver to rule out primary liver disease.
2. 不典型病变 Atypical lesions
3. 体积增大或影像学特征变化 Increase in size or evolving imaging features
4. 结节异质性 Nodule heterogeneity
5. 迟发性肝胆增强MRI低信号 Hypointensity on delayed hepatobiliary contrast-enhanced MRI
当对结节进行活检时,同时对非结节性肝脏进行活检以排除原发性肝病。
推荐进行组织学和分子分析 Recommendations-Histology and molecular analysis
免疫组织化学:在可行的情况下对每个结节进行检查,或对选定的结节进行替代检查(最小组:bcatenin和谷氨酰胺合成酶)。Immunohistochemistry: perform on each nodule whenever feasible or alternatively on selected nodules (minimum panel: bcatenin and glutamine synthetase).
分子分析:在可行的情况下进行HCA亚型分型和评估TERT启动子突变。Molecular analysis: perform HCA subtyping and assess TERT promoter mutations whenever feasible.
四、 所有选项 All the options
闭合前:每6个月进行一次影像学检查(如β-catenin激活或有疑问,每3个月一次)。Pre-closure: perform imaging every 6 months (every 3 months if β-catenin activated or in doubt).
缝合后:每6个月或每年进行一次影像学检查(如果b-连环蛋白激活,第一年每3个月一次,如果很少或没有消退,或有模糊特征,则需要更长时间)。【MCLIN V 2024】
Post-closure: perform imaging every 6 months or once a year for life (every 3 months in the first year if β-catenin activated and for longer if little or no regression, or if equivocal features).
Post-closure: perform imaging every 6 months or once a year for life (every 3 months in the first year if β-catenin activated and for longer if little or no regression, or if equivocal features).