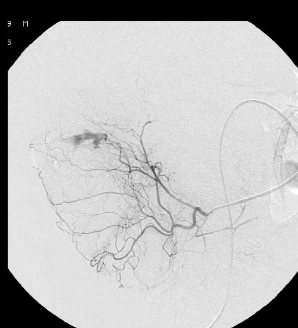
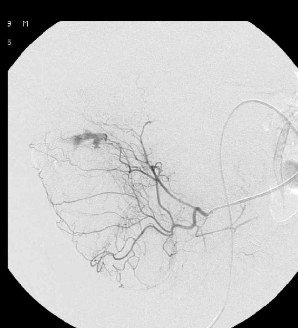
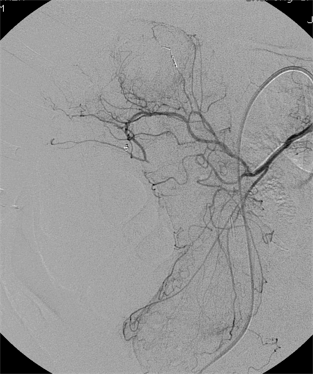
1. 有效降低出血动脉灌注压
2. 促进出血血管的痉挛和血栓形成
3. 防止侧支循环参与供血的潜在可能
4. 减少出血邻近肠道缺血
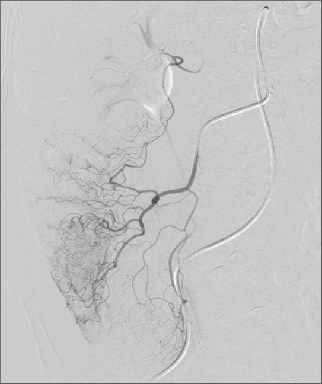
● 弹簧栓子的应用取决于 position of the microcatheter(导管头距出血点距离)
▲ 上消化道出血的壁动脉 in the mural artery (upper GIH),
盲栓胃十二指肠和胃左动脉 (in gastroduodenal, left gastric a. for blind embo)
▲ 在肠系膜动脉 in the mesenterium (lower GIH)
近端:起始动脉至倒数第一弓 proximally: first to last-but-one arc
最后的肠系膜动脉弓 distally: the “last” mesenteric arc
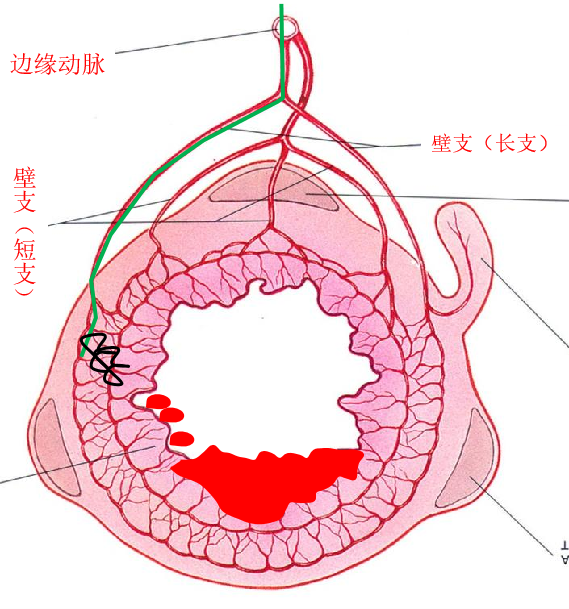
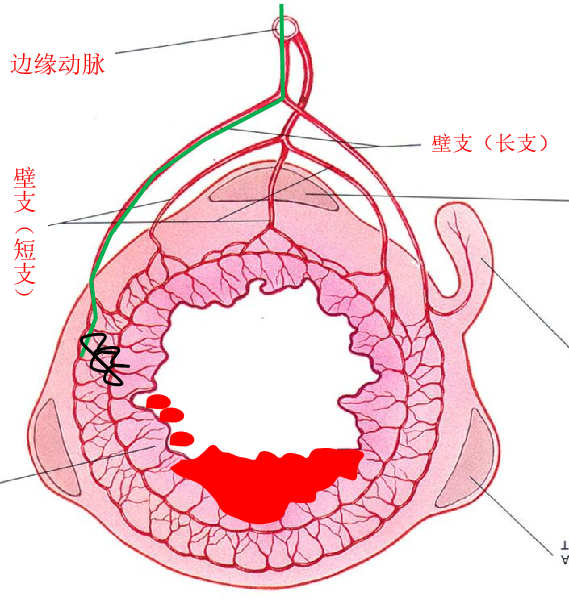
between middle and left colonic arter y= marginal artery of Drummond 边缘动脉
肠壁直动脉 in the bowel wall (vas rectum, straight artery)
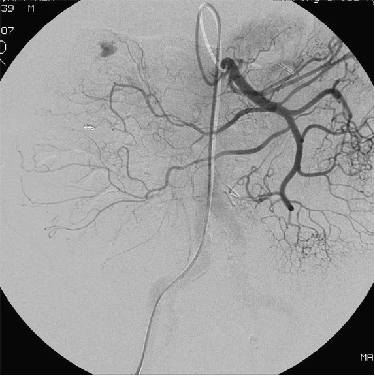
● 微导管在近弓位置 Position of the microcatheter in the proximal arcs
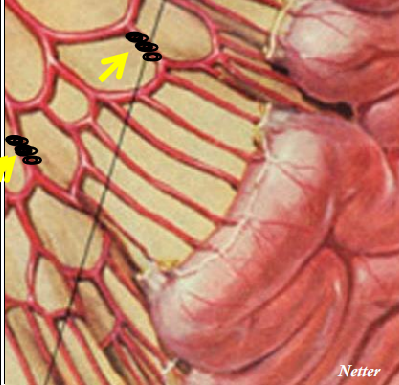
近端:倒数第一个弓: no “good” indication for coils because of collateral supply
微导管在系膜动脉近端动脉弓,不是微弹簧栓子栓塞的“好”的位置。因为可以形成侧支循环
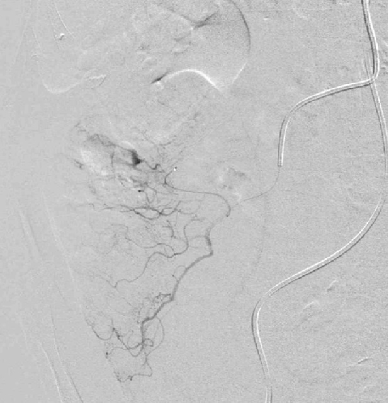
微导管的位置在末梢或边缘动脉
Position of the microcatheter in the distal arc/marginal artery
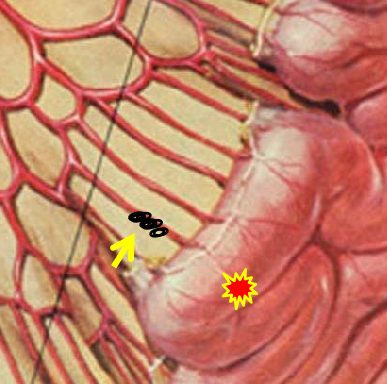
微导管在最后的血管弓或边缘动脉内应该是微弹簧栓子较好的位置,可以降低出血位置的灌注压,有利于血凝块的形成。通过直小血管返流的危险性低
should be a good position:
● to lower blood pressure and enable clot formation
● risk of back flow via vasa recta arcs is lower
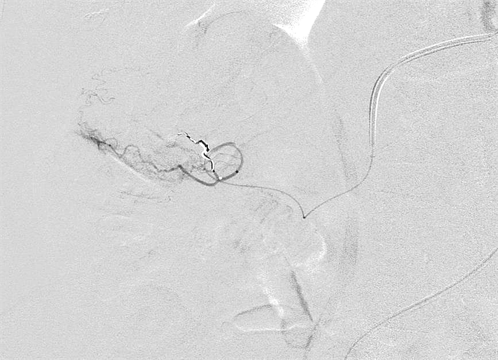
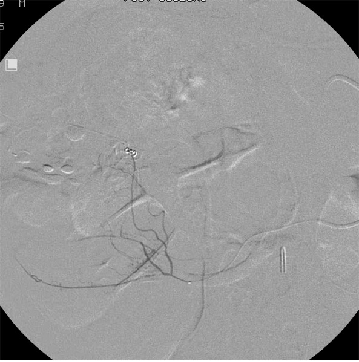
微导管在直小动脉 Position of the microcatheter in the vasa recta
最好的位置 Best position
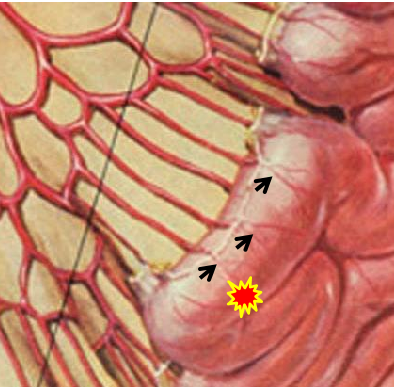
微导管在直小血管内是消化道出血微弹簧栓子栓塞的最好的位置
 |
 |
|
|
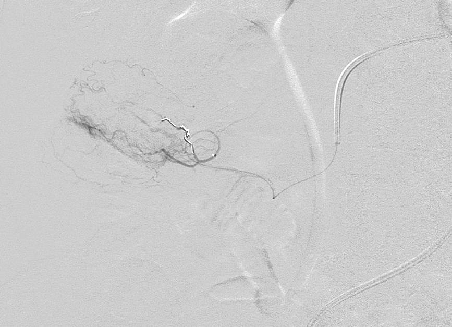
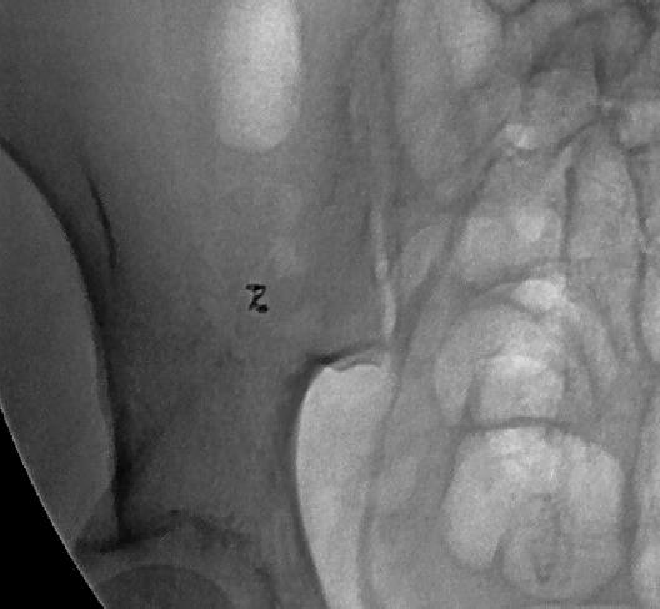
弹簧栓子位于直小动脉内 |
消化道出血弹簧栓子远端栓塞