经皮桡动脉入路出血并发症包括穿刺部位出血和导管路径出血 在讨论经桡动脉路径穿刺的几个焦点问题中,出血是一个重点问题
 
RIFLE (Radial Versus Femoral Randomized)
RCT with 1001 pts. with acute coronary syndrome undergoing
primary/rescue percutaneous coronary intervention
出血并发症发生率低 Lower rate of bleeding complication:
7.8% (桡动脉) vs. 12.2% (股动脉) p=0.026
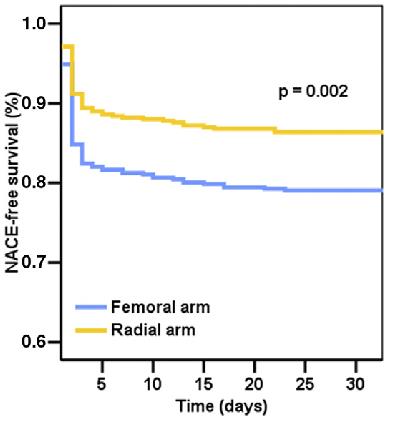
RIFLE-STEACS的结果清楚地显示了STEACS患者在桡动脉入路比股动脉入路方面的优势。这种显著性差异和高成功率应该是使用桡动脉入路治疗急性患者的主要原因。
Minimizing Adverse Haemorrhagic Events by TRansradial Access Site and Systemic Implementation of angioX (MATRIX)
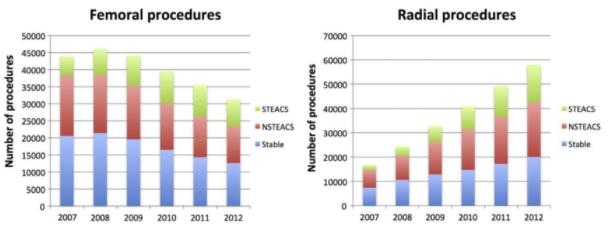
Since 2007 radial access has grown 25% per year in the UK, accounting for > 65% of all PCI’s in 2012
经桡动脉介入放射学应用首次报告
pseudoaneurysm (n=1)
hematoma/bleeding (n=13)
radial artery occlusion (n=11): all asymptomatic
Conclusions: TRA was safe and well tolerated in a heterogeneous patient population across a range of peripheral vascular interventions.
经桡动脉穿刺入路:减少出血和穿刺部位的并发症
• 经股动脉入路出血并发症被报告2%-12%。
• 腹股沟并发症延迟出院或需要治疗占2%
(RA)无论临床状况、患者群体或抗凝状态如何,通路显示出血和通路部位并发症均有统计学意义上的显著减少
Mamas MA, Ratib K, Routledge H et al. Influence of access site selection on PCI-related adverse events in patients with STEMI: meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Heart 98,303–311 (2012).
Retrospective review of contemporary prevalence and outcomes of transradial versus transfemoral access for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) from the US 。 National Cardiovascular Data Registry.
• reduction in bleeding and vascular complications with radial access is particularly pronounced in patients with significant peripheral arterial disease.
出血和血管并发症的减少在有亚种外周动脉疾病的患者中尤为明显。
• Absent femoral pulses, bilateral iliac artery disease, severe vessel calcification or tortuosity, aortobifemoral surgical reconstruction.
缺乏股动脉搏动动,双侧髂动脉疾病,严重血管钙化或迂曲,主动脉双股手术重建的患者。
Kiemeneij F, Laarman GJ, Odekerken D, Slagboom T, Van der Wieken R. A randomized comparison of percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty by the radial, brachial and femoral approaches: the Access study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 29, 1269– 1275 (1997).
文献怎么说? 900例随机随机对照
经肱动脉入路 BA ACCESS
Between January 1, 2003 and December 31, 2017, BA access was used in 157 cases performed on 136 patients. The procedures included 102 (65%) therapeutic interventions and 55 (35%) diagnostic studies. The vessels studied or treated included lower extremity arteries (48), the aorta and iliac arteries (45), mesenteric arteries (45), failing arterial revascularizations (24), renal arteries (9), subclavian arteries (8), carotid arteries (2), and visceral aneurysms (2), or in conjunction with endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR), fenestrated EVAR, or thoracic EVAR (8). More than 1 vessel was studied or treated in 34 cases. Sheath sizes included 5F in 38 (24%) cases, 6F in 93 (59%) cases, and 7F in 26 (17%) cases. Percutaneous puncture was utilized in 142 (90.4%) cases and planned surgical exposure with primary closure of the BA in 15 (9.6%) cases (10, 7F; 4, 6F; 1, 5F). Manual compression was used for hemostasis at the conclusion of all percutaneous cases.
• BA access in 157 cases/136 patients.
• 102 therapeutic/55 diagnostic.
• Sheaths: 5F (24%); 6F (59%); 7F (17%).
• Percutaneous: 90,4%.
• Manual compression
• Access site complications 10,6% [15/142] of percutaneous access cases.
• Open surgical repair for bleeding (8) and thrombosis (7).
In our experience, percutaneous BA access was associated with a 10% complication rate with an increased risk of complications associated with increasing sheath size.
根据我们的经验,经皮BA通路与10%的并发症发生率相关,与鞘大小增加相关的并发症风险增加。
There was approximately the same incidence of bleeding as thrombosis.
出血的发生率与血栓形成的发生率大致相同。
For patients who require 6 or 7F sheaths via a BA approach, we recommend more liberal use of open surgical exposure and primary BA repair.
对于需要通过BA方法进行6或7F鞘的患者,我们建议更自由地使用开放手术暴露和初次BA修复。
|