背景
下消化道出血栓塞 Embolisation for lower GI bleeding
下消化道出血栓塞主张用微弹簧栓子栓塞终末支(直动脉)是因为可以充分的降低出血动脉的灌注压,利于出血点的痉挛和血栓形成,达到止血的目的。
所以弹簧栓子的应用要超选择,所谓How distal does LGIB embolization need to be?
-
空肠,回肠,结肠 Jejunum, ileum, colon
-
直动脉末梢栓塞 Distal embolization of vasa recta (straight artery)
-
超越边缘动脉 Beyond the marginal artery
-
尽可能接近出血的位置 As close as possible to the site of haemorrhage
-
减少肠缺血的危险 Bowel wall ischaemia is unlikely
- <三个直动脉没有危险 3 or fewer vasa recta: not risky
- ≥ 4个直动脉有危险 4 or more vasa recta: risky
那么,液体栓塞剂在下消化道出血栓塞中的角色是什么呢?
1. 什么时候和如何在下消化道出血的情况下使用液体栓塞剂栓塞
2. 下消化道出血液体栓塞剂的优缺点
3. 下消化道出血液体栓塞剂的结果和并发症
液体包括哪些?
NBCA:Acrylic glues: n-butyl cyanoacrylates = N-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate
Onyx:Onyx Liquid Embolic System
- Polymere: Ethylene-vinyl
- alcohol copolymer (EVOH)
- Solvent: Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) solvent
- Radiopacifying: Micronized tantalum powder
|
Glue
|
Onyx |
|
Polymerizes
|
Precipitates
|
|
No controlled release |
Controlled release |
|
nflammation +++ |
Inflammation (+) |
|
Hard cast |
Sponge-like cast |
|
Free flow |
Free or blocked flow |
|
Fast release |
Slow release |
|
Sticks to catheter |
Does not stick to catheter |
|
Adhesive |
Cohesive |
|
Cheap
|
Expensive |
Loffroy et al. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2009;7:250-63
EVOH
其它?
液体栓塞剂理论上优点
-
高穿透性 Highly penetrable
-
阻塞效果不取决于凝血参数 Occlusive effect does not depend on coagulation parameters
-
止血效果好 High hemostatic effect
-
严重出血效果好 Interesting for massive bleeding
-
能够到达远端较少依赖导管导引 Can reach distal targets that can not be navigated with catheters
-
微导管容易通过 Best option with neuro microcatheters
下消化道出血栓塞什么时候用液体栓塞剂?
-
患者有凝血功能障碍 Coagulation disorders
-
严重的局部出血 Massive focal bleeding
-
直径小和迂曲的血管 Small sized and tortuous vessels
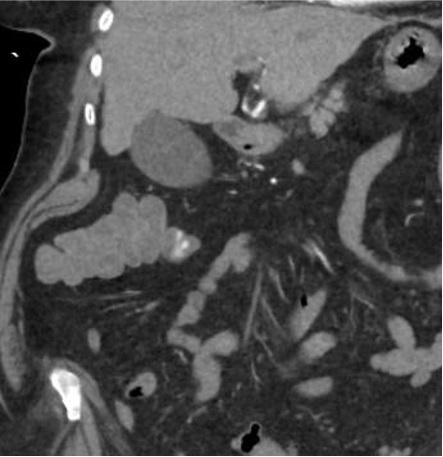
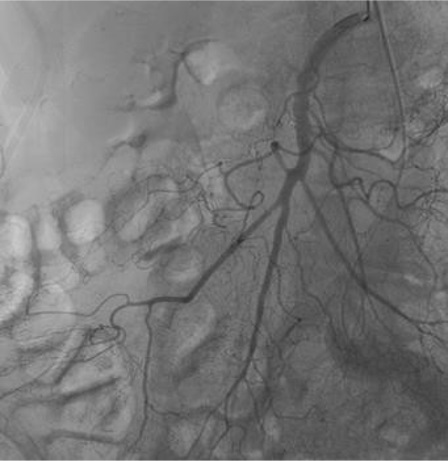
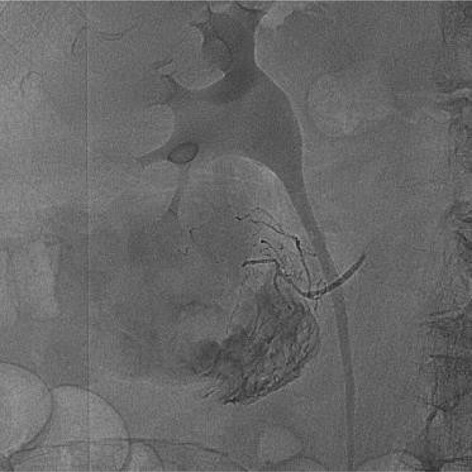
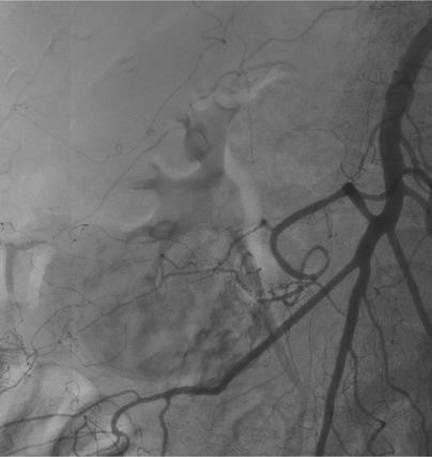
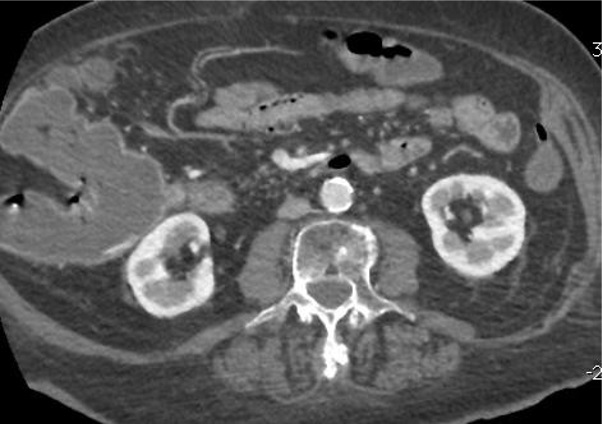
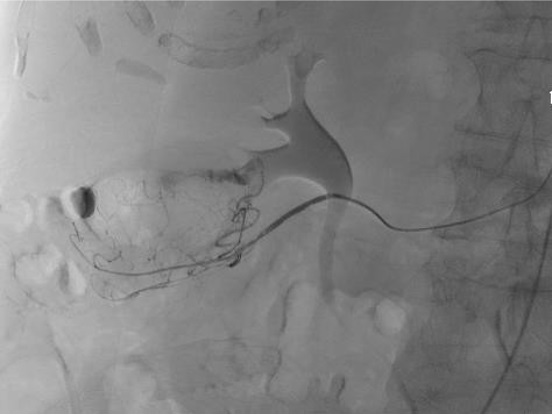
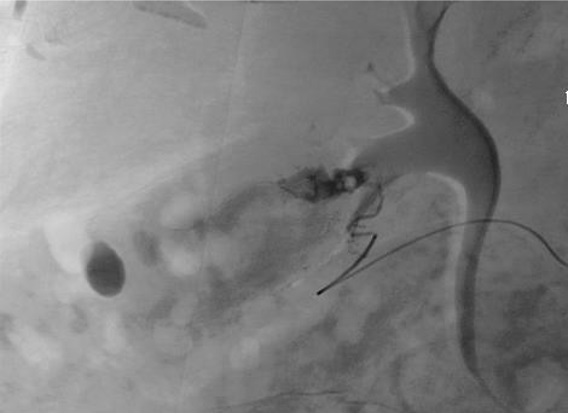
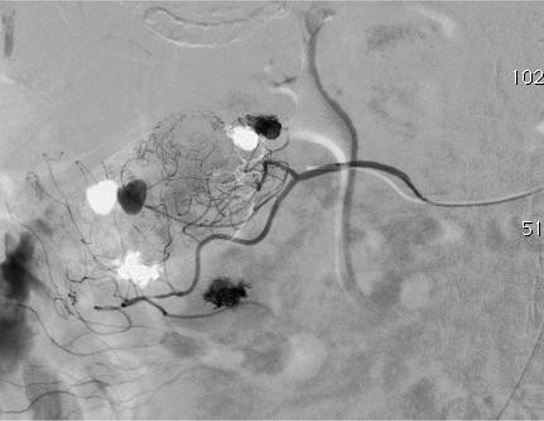
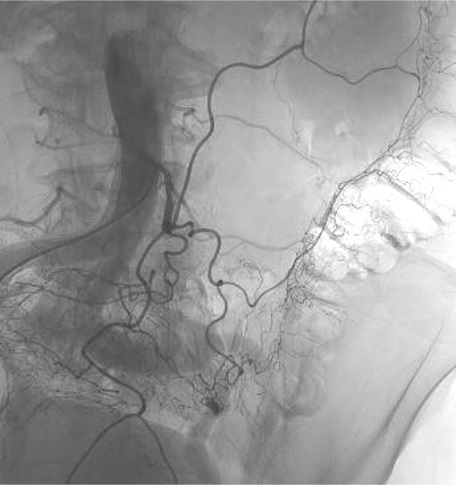
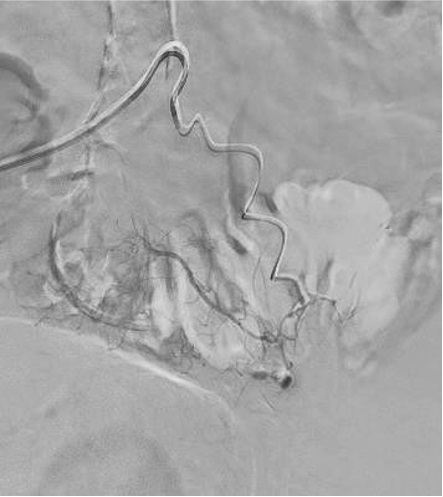
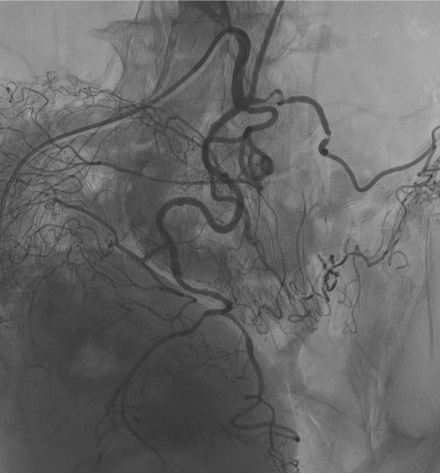
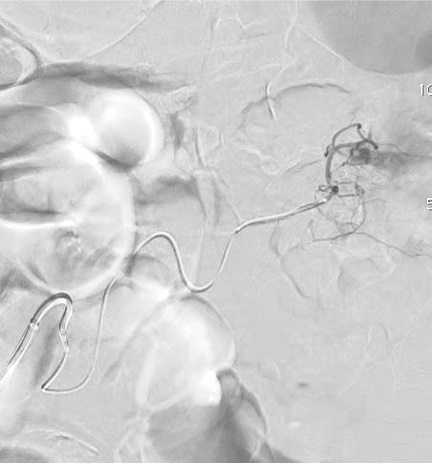
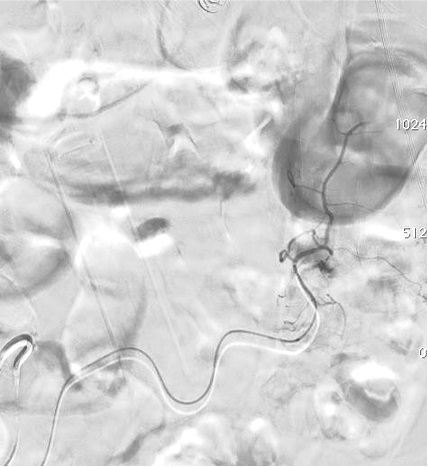
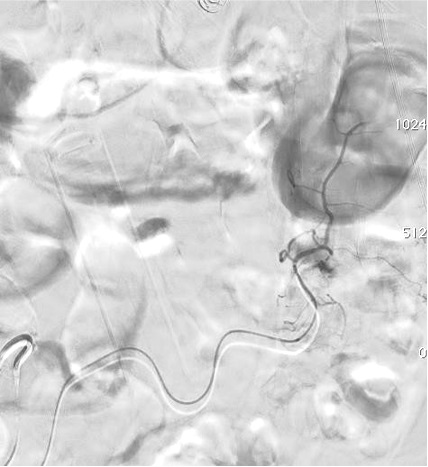
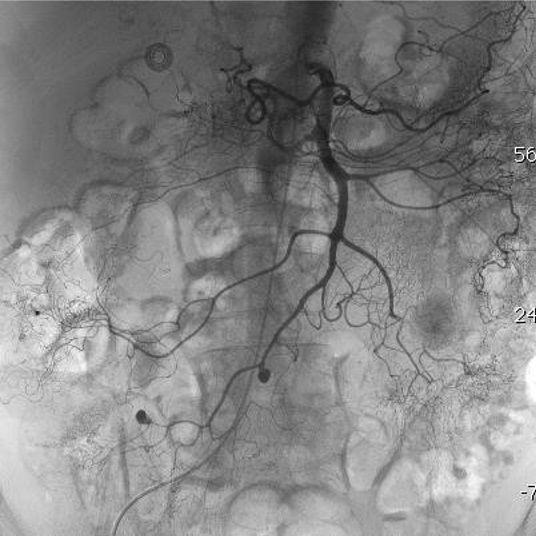
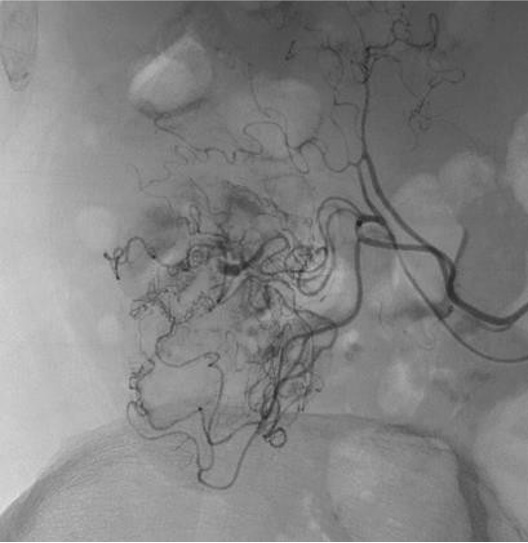
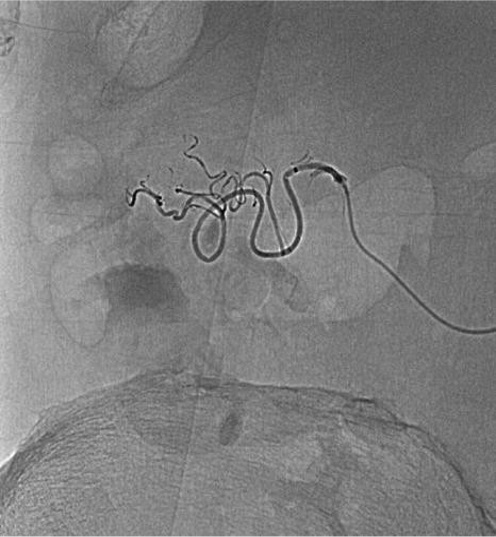
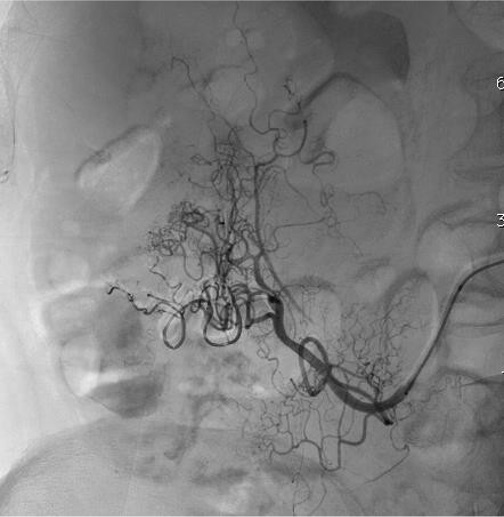
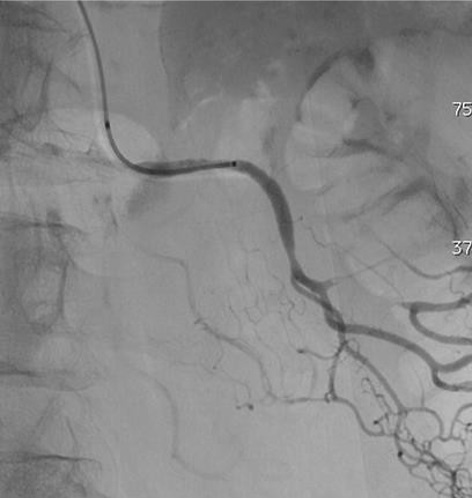
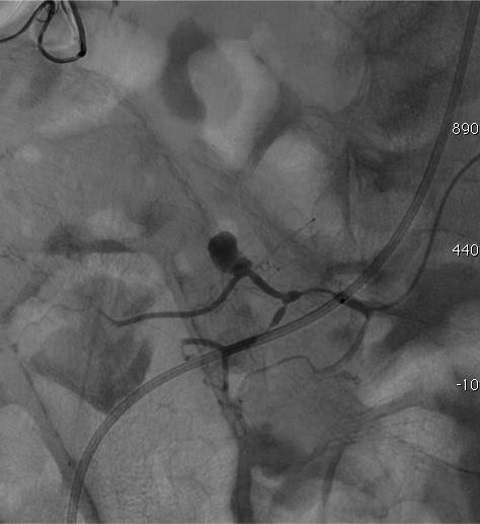
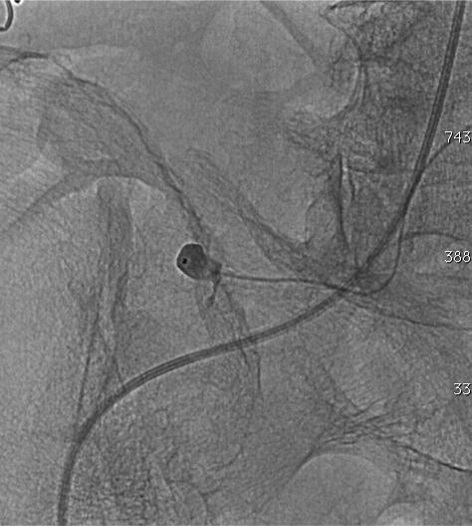
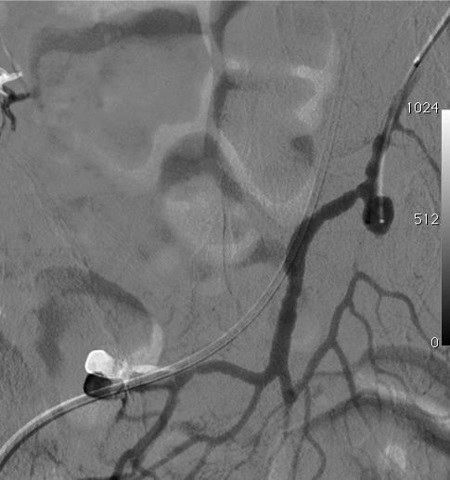
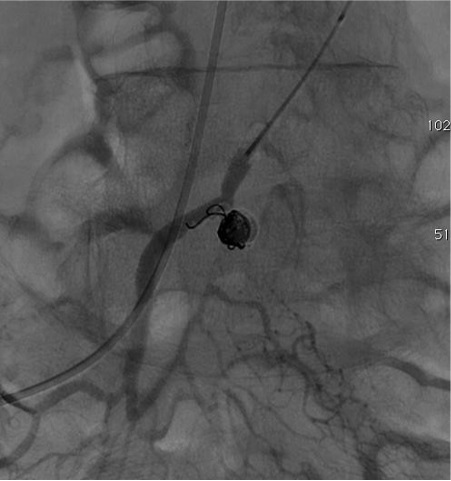
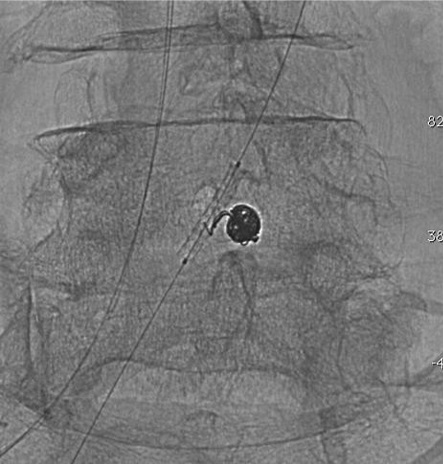
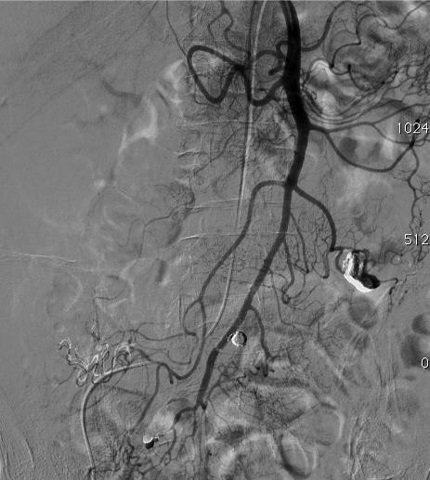
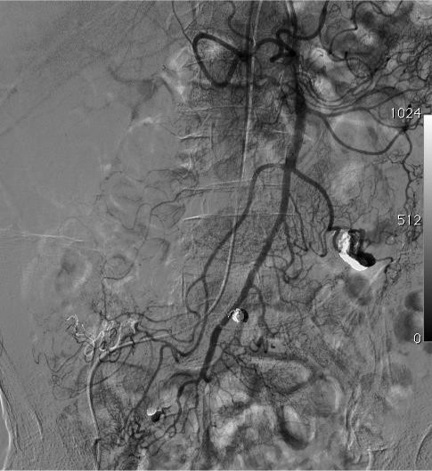
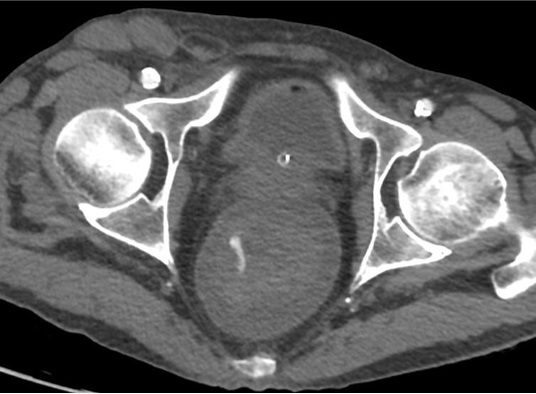
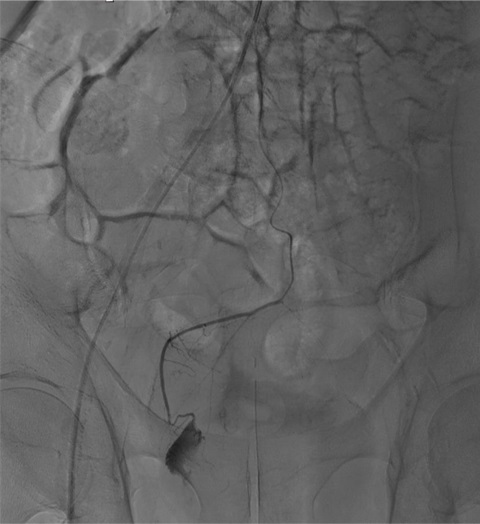
病例一
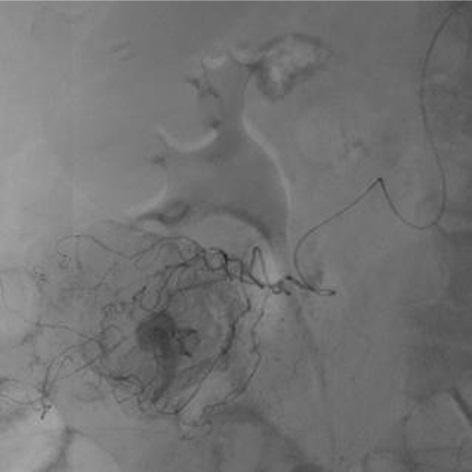
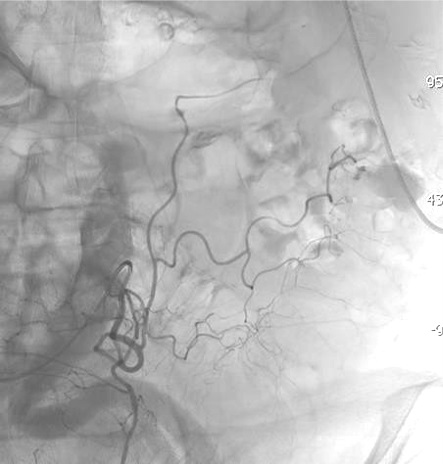
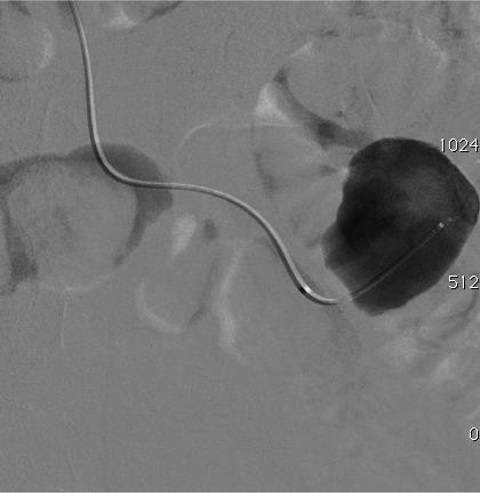
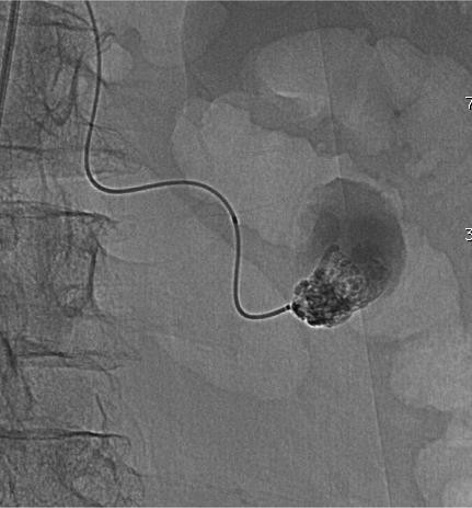
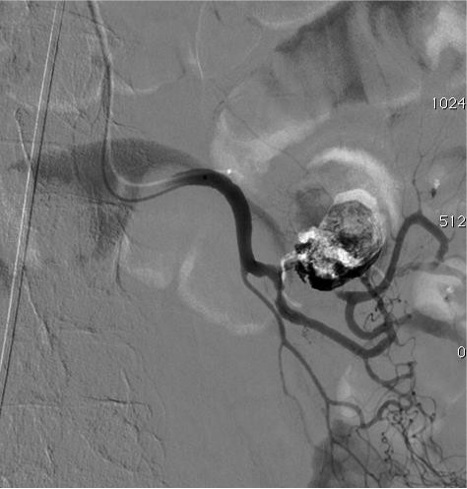
病例二 Onyx
下消化道出血栓塞液体栓塞剂如何用?
-
标准4或5Fr导管 Standard 4 or 5-Fr catheter
-
微导管选择到尽可能的远端 Microcatheter as distal as possible
-
注射Onyx之前用5%葡萄糖水或MDSO冲洗 Previous flushing with G5% or DMSO
-
1-3ml带锁扣的注射器注射 1 or 3 mL luer-lock syringe for injection
-
用碘油调整聚合的速率 Use Lipiodol to modulate the rate of glue polymerisation
-
在透视下缓慢注射Slow and regular injection under strict fluoroscopic control
-
快速去除微导管 Prompt removal of microcatheter with glue
-
血管近端对照造影 Final proximal control angiography
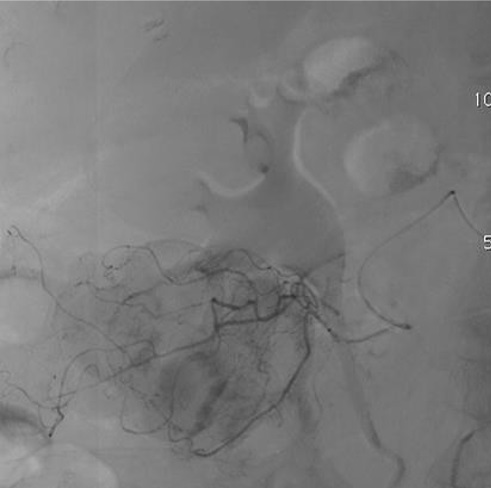
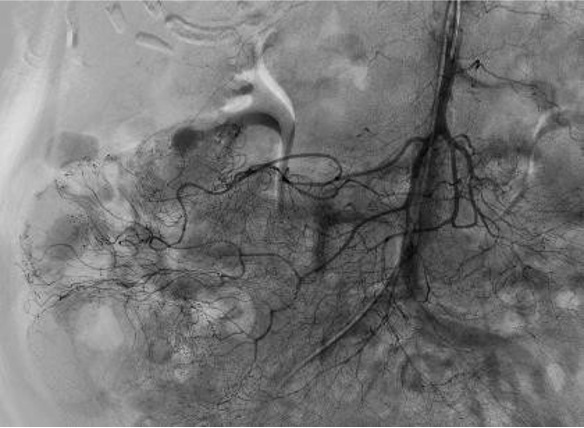
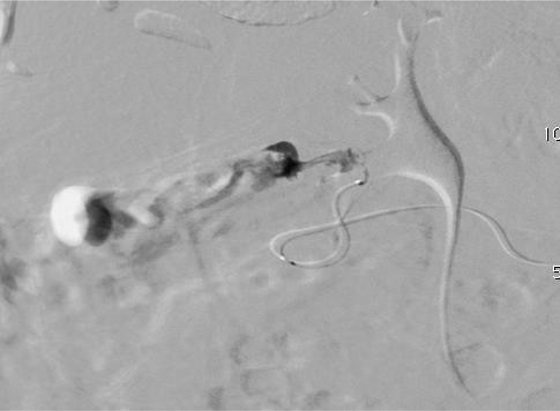
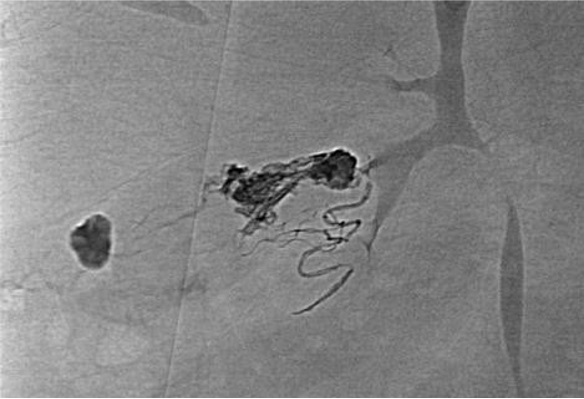
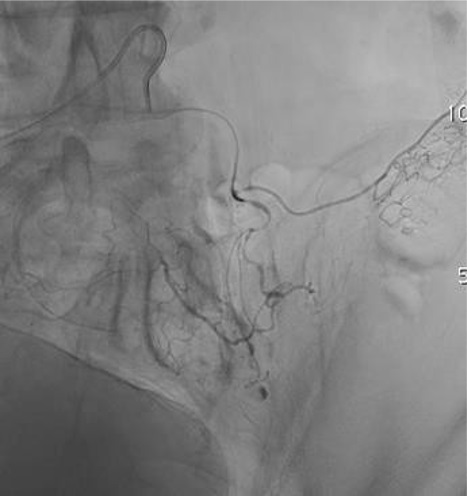
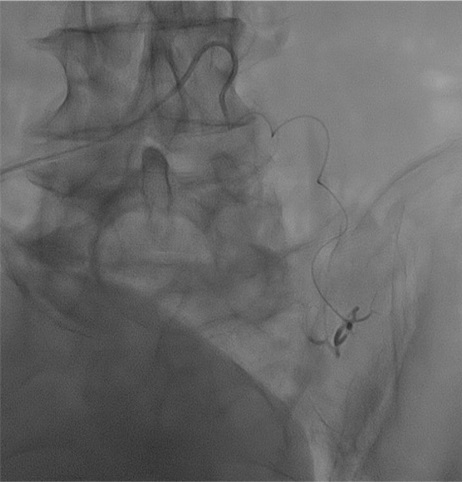
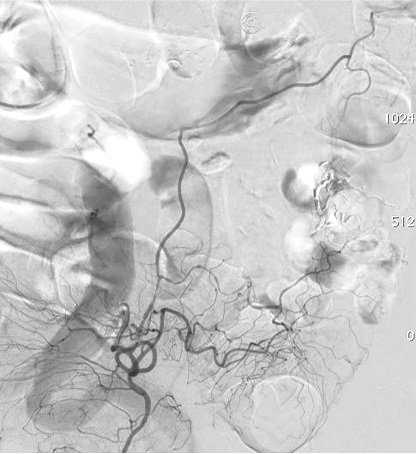
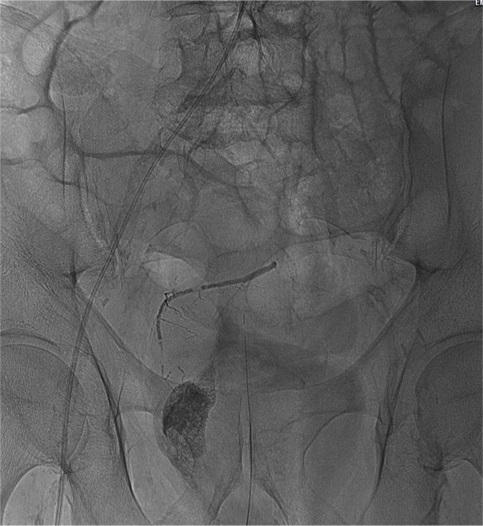
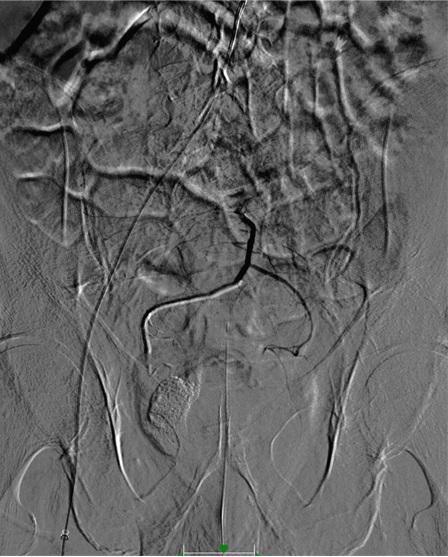
病例三:Front and back door embolization with Onyx
病例四:Also possible with Glubran2 (< 4 vasa recta)
液体胶的缺点(Drawback)
学习曲线 Learning curve:
- 稀释 Dilution (glue ++)
- 理想注射 Optimal injection
- 并发症预防 Prevention of complications:
+ 导管粘连 Sticking catheter:
Glue >> Onyx
+ Ischemic risk:
Glue = Onyx
+ Non target occlusion:
Glue > Onyx
强力胶水

液体栓塞剂的结果
消化道出血最常见应用微弹簧栓子、500-700μmPVA,明胶海绵粉,但在严重出血的情况下,胶或Onyx应该考虑,但是否增加肠缺血是值得进一步探讨的事。总的来说下消化道出血栓塞严重的肠缺血需要外科的大约2%。
Outcomes of LGIB embolization with ONYX
|
|
UGIB |
LGIB |
Technical success |
Clinical success |
Re bleeding |
Major complications |
30-day mortality |
|
Lenhart Eur Radiol 2010 |
10 |
6 |
100% |
81% |
6.2% |
0% |
12.5% |
|
Urbano JVIR 2014 |
0 |
31 |
93.5% |
96.7% |
10% |
0% |
6.4% |
|
Sun Indian J Cancer 2015 |
7 |
2 |
100% |
100% |
0% |
0% |
0% |
39例下消化道出血没有严重肠缺血
|
|
UGIB |
LGIB |
Technical success |
Clinical success |
Re bleeding |
Major complications |
30-day mortality |
Frodsham
JVIR 2009 (T) |
0 |
14 |
100% |
79%
|
21% |
0% |
7.1% |
Huang
JVIR 2011 (H) |
0 |
27 |
100% |
67% |
14.8% |
0% |
33% |
Yata
JVIR 2013 (H) |
16 |
23 |
100% |
95% |
5% |
8.1% |
21.6% |
Hur
JVIR 2014 (?) |
0 |
84 |
100% |
75.3% |
15.2% |
4.8% |
26.2% |
Koo
AJR 2015 (H) |
72 |
30 |
100% |
76.5% |
15.7% |
1.9% |
8.8% |
Kodani
JVIR 2016 (?) |
0 |
16 |
100% |
93.8% |
6.2% |
12.5% |
0% |
Zhao
Gastr Res 2016 (?) |
0 |
7 |
100% |
85.8% |
14.2% |
0% |
0% |
201例下消化道出血栓塞的病人,4例肠缺血需要外科手术,=1.99%
Cavity filling Controlled sandwich (Onyx+++)
Onyx
|