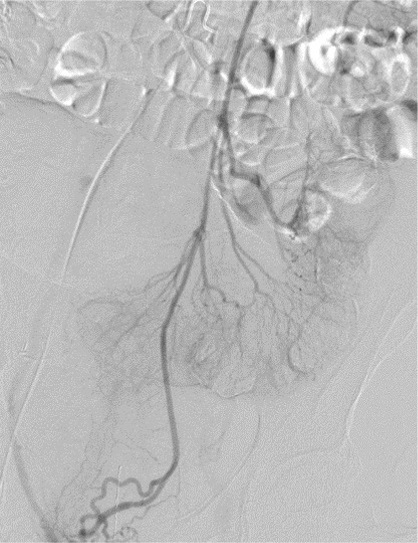
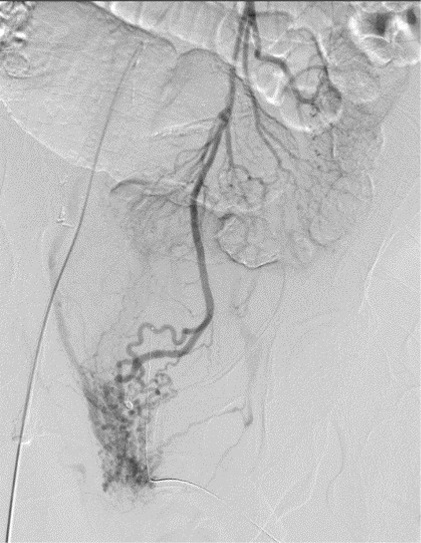
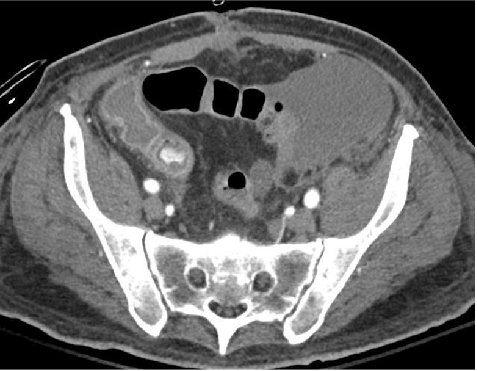
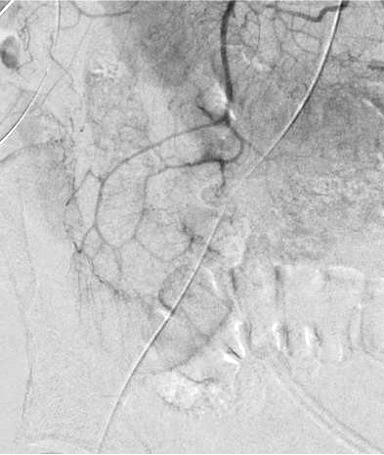
Optical Colonoscopy
赞成 PROS:
-
应该成为下消化道出血最初始诊断方法 It should be initial diagnostic procedure for LGIG
-
同时兼具诊断和治疗的作用 Diagnostic and therapeutic role
-
活检可能 Biopsy is possible
-
直接观察结肠粘膜 Direct colonic mucosa visualization
缺点 CONS:
-
不能用于生命体征不稳定的病人 Not possible in hemodynamically unstable patients
-
不可能或不能用于没有结肠准备的病人 Not possible or not useful without colon preparation
-
不能用于小肠出血的结肠 Not useful for small bowel
-
不能每天24小时应用 Not always available 24h/7d,有限医院具备胃肠镜夜间值班医生
-
侵入性检查(穿孔危险)It is invasive (risk of perforation)
-
治疗后再出血25% rebleeding rate after therapeutic procedure
Multidetector CT (MDCT)
-
▲不需要准备 No preparation is required & 24/7
-
▲ 非侵入性 Non-invasive
-
▲ 精确信息 Accurate information:
-
▲ 存在或缺乏活动性出血 Presence or absence of active bleeding
-
▲ 出血的位置,来源和病因 Bleeding site, source and cause
-
▲ 显示完全的血管解剖 Displays complete vascular anatomy
-
▲ 高度敏感 High sensitivity (0,3 ml/min)
-
▲ 检查范围包括小肠和结肠 Small bowel and Colon
-
▲ 可复制和可重复 Reproducible and Revisable
-
▲ 没有活检取样的机会 No chance for biopsy sampling
-
▲ 面膜观察能力差 Poor mucosal visualization
-
● 多期检查分析 Multiphasic studies
-
● 检查时间 :可能的话,活动出血的时候 When: During active hemorrhage if possible
-
● 包括完全的腹部和盆腔 Include complete abdomen and pelvis
-
● 无需口服造影剂 No oral contrast
-
● 1毫米层厚 1 mm thickness slice
-
● 4毫升/秒+50ml 盐水 高压注射器注射 Power injector at 4ml/s rate plus 50 ml of Saline
-
● 100-125毫升造影剂 100 – 125 ml of contrast (≥ 300 mg/ml of iodine)
-
● 自动団注触发 Automated bolus triggering (150 HU threshold)
MDCT: Findings on Acute GI Bleeding
-
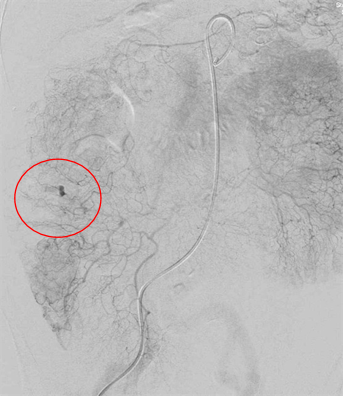
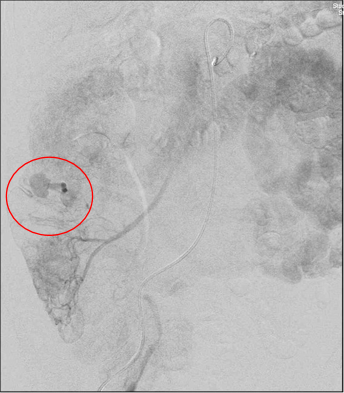
● 活动性出血:染色 Active bleeding: blush
-
● 最近出血:高CT值血凝块(≥90) Recent bleeding: hyperattenuating clots (≥90 HU)
-
● 造影剂外溢改变表现 Changing appearance of the extravasated contrast
-
● 静脉期活动性出血更大和更明显 Active bleeding is larger and more intense in venous phase
-
● 静脉早起引流:血管发育不良 Early-draining veins: angiodysplasia
-
● 最大密度投影:血管解剖 MIP reformations: Vascular anatomy
-
● 注意陷阱 Be careful with pitfalls
99m Tc-labeled red blood cells
-
最敏感的影像学方法 Most sensitive imaging method
-
花费时间 Time consuming
-
不能够精确定义出血的解剖来源 It is not able to define precisely the anatomic source of the bleeding
-
适合隐匿性和间断消化道出血 Indicated for Obscure and Intermittent GI Bleeding
-
适合当内镜或MDCT为阴性时候 Indicated when findings of endoscopy and MDCT are negative
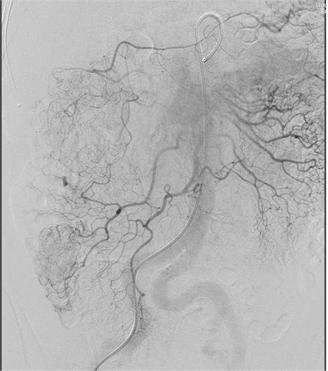
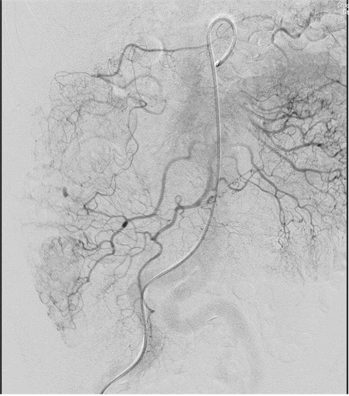
DSA (cone beam CT, automatic vessel detection software)
Enteroscopy
Videocapsule endoscopy
隐匿性消化道出血的金标准 Gold standard for Obscure GI Bleeding
-
☑ 非创伤性 Non-invasive
-
☑ 阳性结果 70% Positive results: 70%
-
☑ 消耗时间 Time consuming
-
☑ 不能获取活检 No ability to obtain biopsy
-
☑ 并发症≤ 1% Complications ≤ 1%
结论
✔ 急性上消化道出血,首先是胃镜(Acute UGIB: endoscopy first)
✔ 急性下消化道出血,MDCT优先(尽管没有指南)Acute LGIB: MDCT first (no guidelines yet)
✔ 没有肠道准备的结肠镜没用或没可能 (Colonoscopy without bowel preparation is not useful or possible)
✔ DSA之前 增强CT(Multiphase MDCT without oral contrast always before DSA)
✔ 下消化道出血栓塞和外科治疗是针对靶向目标治疗 (LGIB embolization and surgery are target therapies)
✔ 危及生命的下消化道出血栓塞优先选择(Embolization is the first option for life threatening LGIB)
.
✔ 阳性CT表现,不足以表明适合下消化道出血的栓塞治疗 (A positive MDCT is not enough to indicate a LGIB embolization)
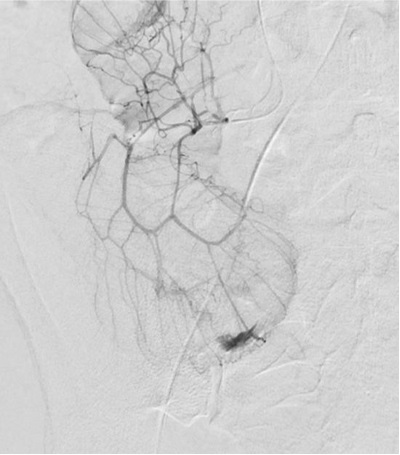
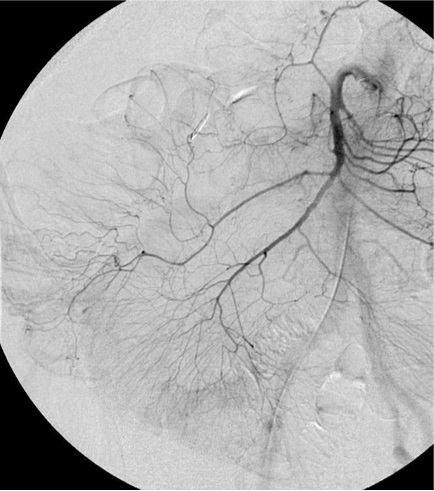
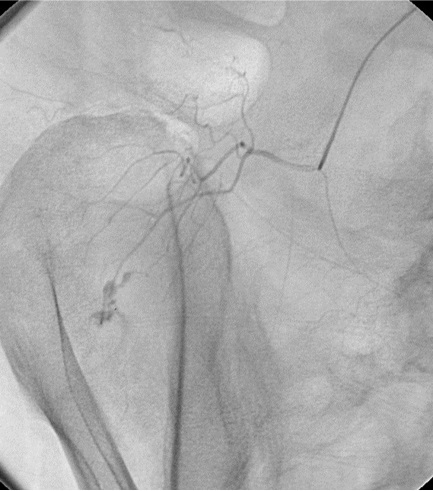
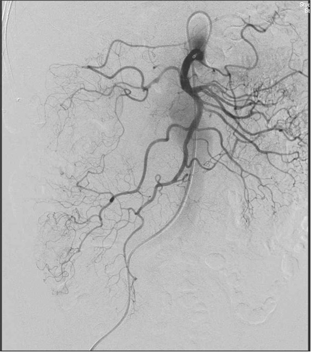
无论如何高质量动脉造影图像(DSA)的获取是下消化道出血栓塞的关键因素
▲ 导管位置固定 Have catheter well seated,在注射造影剂情况下,有时导管会向后撤
▲ 注射足够的造影剂 Inject enough contrast
▲ 胰高血糖素Glucagon或 654-2 抑制肠蠕动(bowel paralysis)
▲ 憋气 , breath holding,
▲ 肠内内充气 air infufflation
▲ 确定解剖部位全覆盖 Make sure to cover the anatomic distribution,小一点的影像增强器可能不能全覆盖,降低管球或多次采集摄影
不能全覆盖 failure to cover full extent of artery)
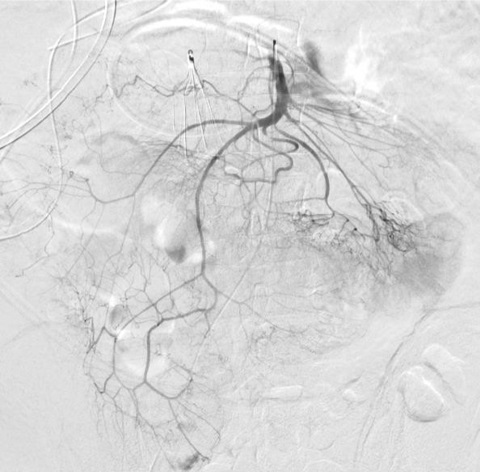 |
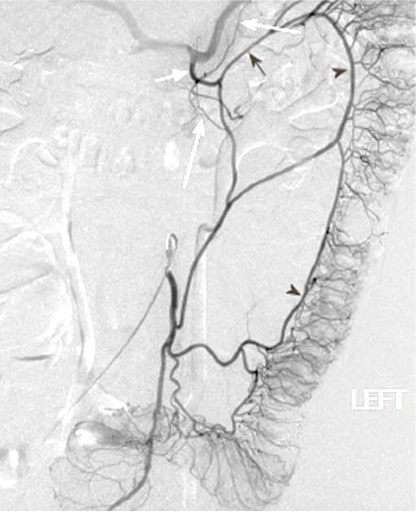 |
|
出血点险些出覆盖范围(最下方)
|
右结肠动脉出自腹腔动脉,痣上动脉在范围之外 |
中心太靠上 Failing to Center Low Enough
▲ 如果出血没有发现再注射 Re-inject if bleeding not seen initially
▲ 使用短促呼吸 Use breathing runs (不能憋气者)
▲ 先肠系膜下动脉,再肠系膜上动脉,避免肾盂或膀胱显影影像观察
▲ 全麻下停呼吸,如果可能的话,最好
肠蠕动抑制,高质量的血管造影
|