Venous malformations are very commonly encountered [ɪn'kaʊntəd] in interventional radiologic practice.
静脉畸形在介入放射学实践中非常常见。
Indications for therapy are clearly defined [dɪ'faɪnd] based on the lesion's impact on patient's quality of life.
治疗的适应症是根据病变对患者生活质量的影响来明确定义的。
Screening laboratory coagulation studies in patients with historical [hɪˈstɒrɪkl] or lesion morphologic risk factors often reveal abnormal coagulation parameters [pə'ræmɪtəz] consistent with localized intravascular coagulation* or more severe coagulo'pathic states.
带有相关病史或病变形态学表现危险因素的患者进行凝血相关化验筛查常显示凝血异常,伴有局部血管内凝血或更严重的凝血异常状态
These may require chronic or periprocedural medical management to avoid potentially life-threatening disseminated intravascular coagulation or other thromboembolic phenomena [fɪˈnɑmənə].
这些可能需要长期或围手术期的医疗管理,以避免潜在的危及生命的弥散性血管内凝血或其他血栓栓塞现象。
Once a multidisciplinary [ˌmʌltidɪsəˈplɪnəri] decision to treat a venous malformation is made, one must decide between percutaneous and/or surgical techniques.
一旦多学科讨论决定治疗静脉畸形,就必须决定经皮和/或外科技术。
Sclerotherapy with adjunctive stasis of efflux ['eflʌks] (STASE) techniques have become the mainstay of therapy for most venous malformations as they are well-tolerated [ˈtɔləreitid] and effective.
流出停滞(STASE)技术的硬化治疗已成为大多数静脉畸形的主要治疗手段,因为它们耐受性好,效果好。
STASE techniques work primarily by the administration of sclerosant [sklɪə'rəʊzənt] (s) exerting [iɡˈzə:tɪŋ] an inhibitory and/or endotheliocidal effect on venous malformation endothelium [ˌendəʊ'θi:lɪəm] leading to thrombosis, involution ['ɪnvə'lju:ʃən] 消退,退化, and fibrosis, and secondarily via adjunctive outflow occlusion using any combination of local compression, balloons, gelatin[ˈdʒelətɪn], coils, laser, radiofrequency, or adhesives [æd'hɪsɪvz] to improve sclerosant penetration and dwell-time (停留时间)in the lesion.
STASE技术的主要作用是
使用硬化剂对静脉畸形内皮产生抑制和/或内皮杀灭作用,导致血栓形成、退化和纤维化,其次是使用局部压迫、球囊、明胶、线圈、激光、射频或粘合剂激光、射频或粘合剂,以改善硬化剂的渗透和停留时间。 Adhesives [æd'hɪsɪvz] alone can fill the lesion to facilitate [fəˈsɪlɪteɪt] surgical resection in some cases. 单独使用粘合剂可以填充病变,以便在某些情况下进行手术切除。
Common sclerosants in modern practice include sodium tetradecyl [tetrə'desɪl] sulfate[ˈsʌlˌfet], bleomycin, polidocanol [pɒlɪdəʊ'kænəl] , ethanol [ˈeθənoʊl], and hypertonic [ˌhaɪpə'tɒnɪk] saline [ˈseɪlaɪn] .
现代实践中常见的硬化剂包括硫酸十四烷基钠、博莱霉素、吡哆醇、乙醇和高渗盐水。
Most agents can be given directly in unmodified unmodified or “neat [niːt] ” form or can be mixed with a gas to form a sclerofoam or embolic such as gelatin to form a sclerogel.
大多数药物可以直接以未经修饰或“整齐”的形式给予,也可以与气体混合形成硬化剂或栓塞,如明胶,形成硬化凝胶。
Choice and method of sclerosant delivery in each patient is based on
1. the intraluminal lesion volume 2. architecture 3. vital structure proximity 4. agent toxicity 5. viscosity [vɪ'skɒsətɪ] 6. level of experience of the interventional radiologist with that particular agent.
每个患者的硬化剂给药的选择和方法是基于
1. 腔内病变体积 2. 结构 3. 关键结构的接近 4. 栓塞剂的毒性 5. 粘稠度 6. 介入医生使用某种栓塞剂的经验水平
Multi-session STASE therapy usually reduces symptoms of chronic pain or mass with low risk of known complications of skin or nerve impairment [ɪmˈpermənt] , compartment [kəmˈpɑːrtmənt syndrome, hemoglobinuria [ˌhi:məˌgləʊbɪ'nʊərɪə] , deep venous thrombosis, or pulmonary phenomena.
多次STASE治疗通常减少慢性疼痛或肿块的症状,低风险的已知并发症的皮肤或神经损害,室间综合征,血红蛋白尿,深静脉血栓形成或肺部改变(现象)。
Sclerotherapy with Adjunctive Stasis of Efflux (STASE): Techniques and Strategies 
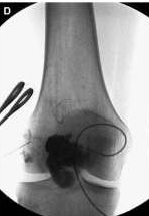
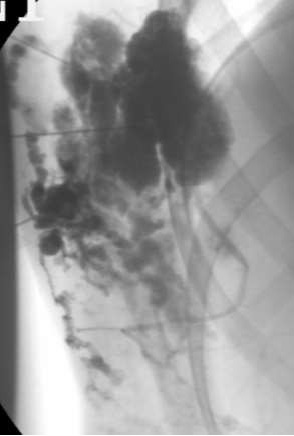
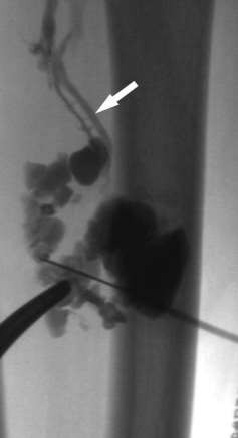
入路后:After access
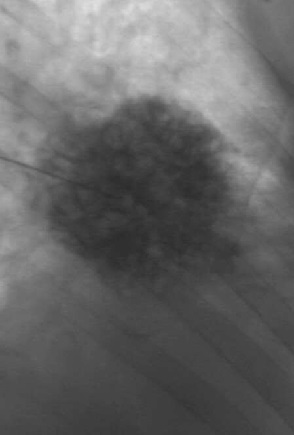
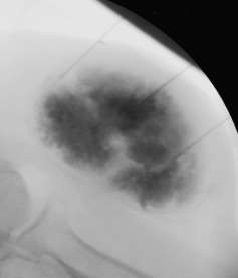
硬化前:Before sclerotherapy: Phlebography 静脉造影:Phlebography

1. Legiehn GM, Heran MK. Venous malformations: classification, development, diagnosis, and interventional radiologic management.Radiol Clin North Am. 2008 May;46(3):545-97, vi.
2. Legiehn GM, Heran MK. Classification, diagnosis, and interventional radiologicmanagement of vascular malformations. Orthop Clin North Am. 2006 Jul;37(3):435-74, vii-viii. Review.
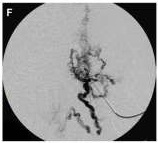
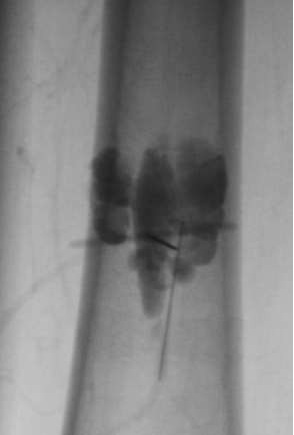
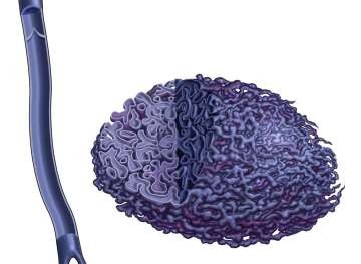
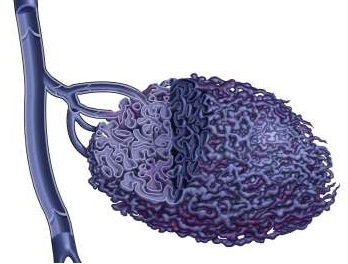
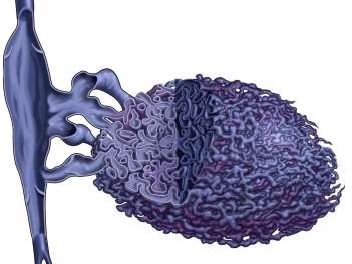
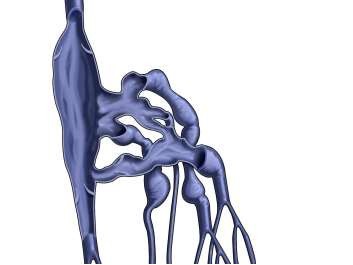
Venous Efflux Patterns This figure represents different phlebography pattern of venous malformation
|