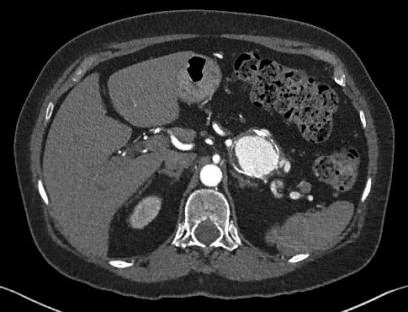
脾动脉瘤虽然罕见,但它是内脏动脉瘤最常见的血管病变。经常是偶然发现。大多数无症状。通常被认为
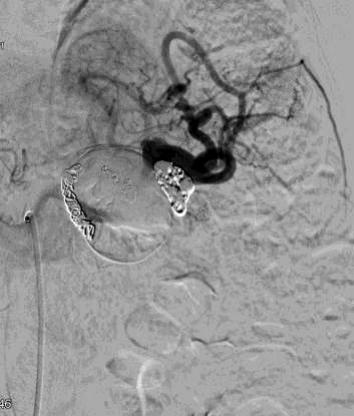
如果发生破裂,有较高的死亡率 脾动脉瘤在门脉高压患者中发病率为7-17%【Moon DB 2009】。这主要归结于肝硬化的患者脾动脉血流速度增加。如果门静脉高压,预期开腹脾动脉瘤切除患者的死亡率较高, 56% vs 17%【Lee PC 1999】。经动脉内治疗脾动脉瘤是目前标准的治疗。
一项比较肝硬化脾动脉瘤和非肝硬化脾动脉瘤栓塞后的结果 Outcomes
The technical success of SAA embolization is 90% orhigher in most series [1–7, 15–17]. The main complications of SAA embolization include splenic infarction and
infection. Although splenic ischemia and postembolization syndrome have been reported in up to 40% of patients undergoing SAA embolization, there have been few clinical
sequelae or evidence of hematological changes due to splenic insufficiency [17, 20]. This is explained by the fact that sufficient perfusion of the spleen occurs from collateral
flow through the short gastric arteries and from the gastroduodenal artery via the gastroepiploic arteries. There is little evidence to suggest that splenic embolization has any
major long-term effect on immune function. However, meningococcal, pneumococcal, and Haemophilus influenzae vaccination is often administered if extensive distal
embolization is performed [25].
|