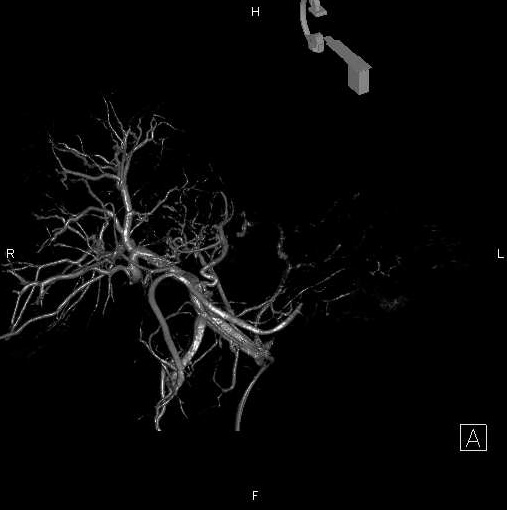
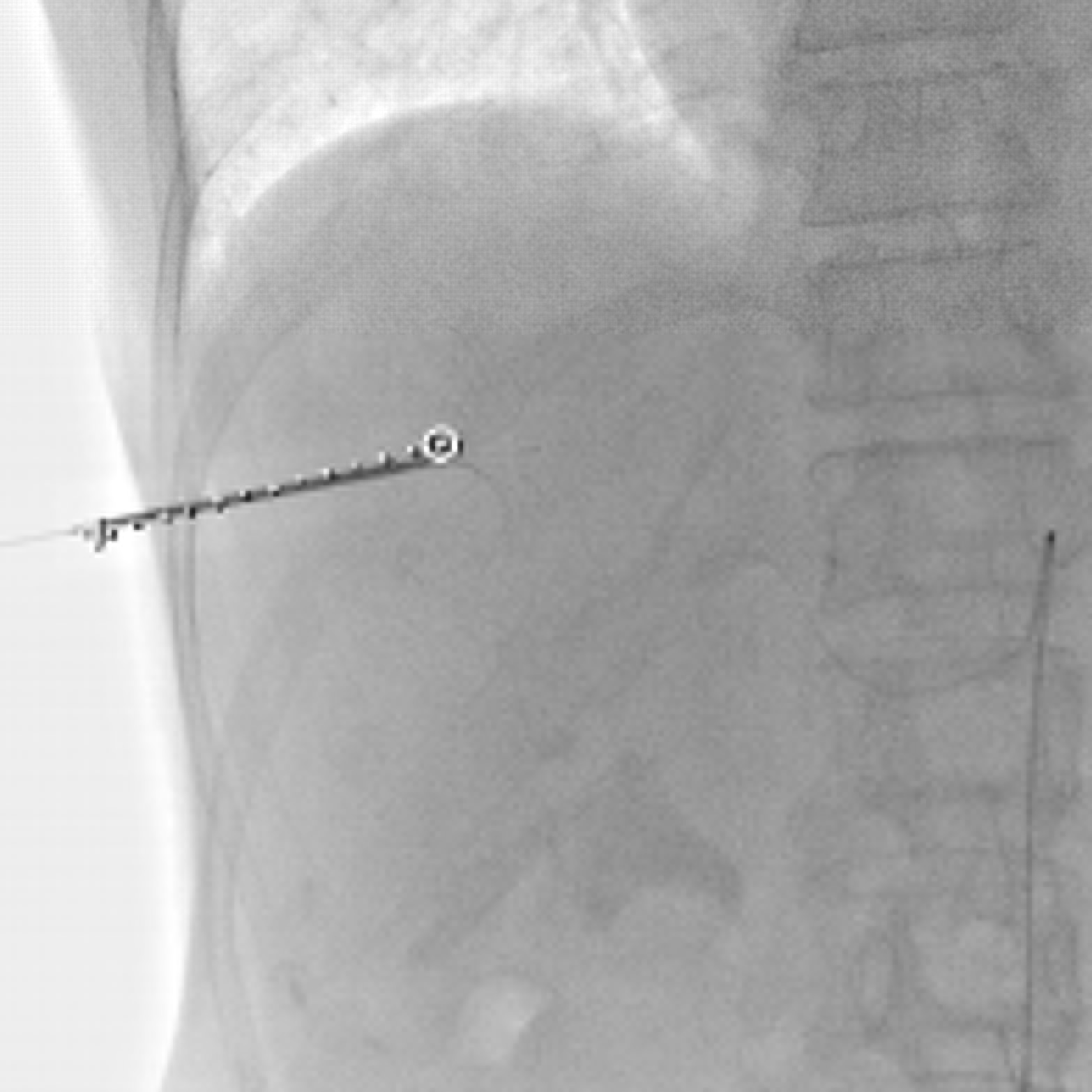
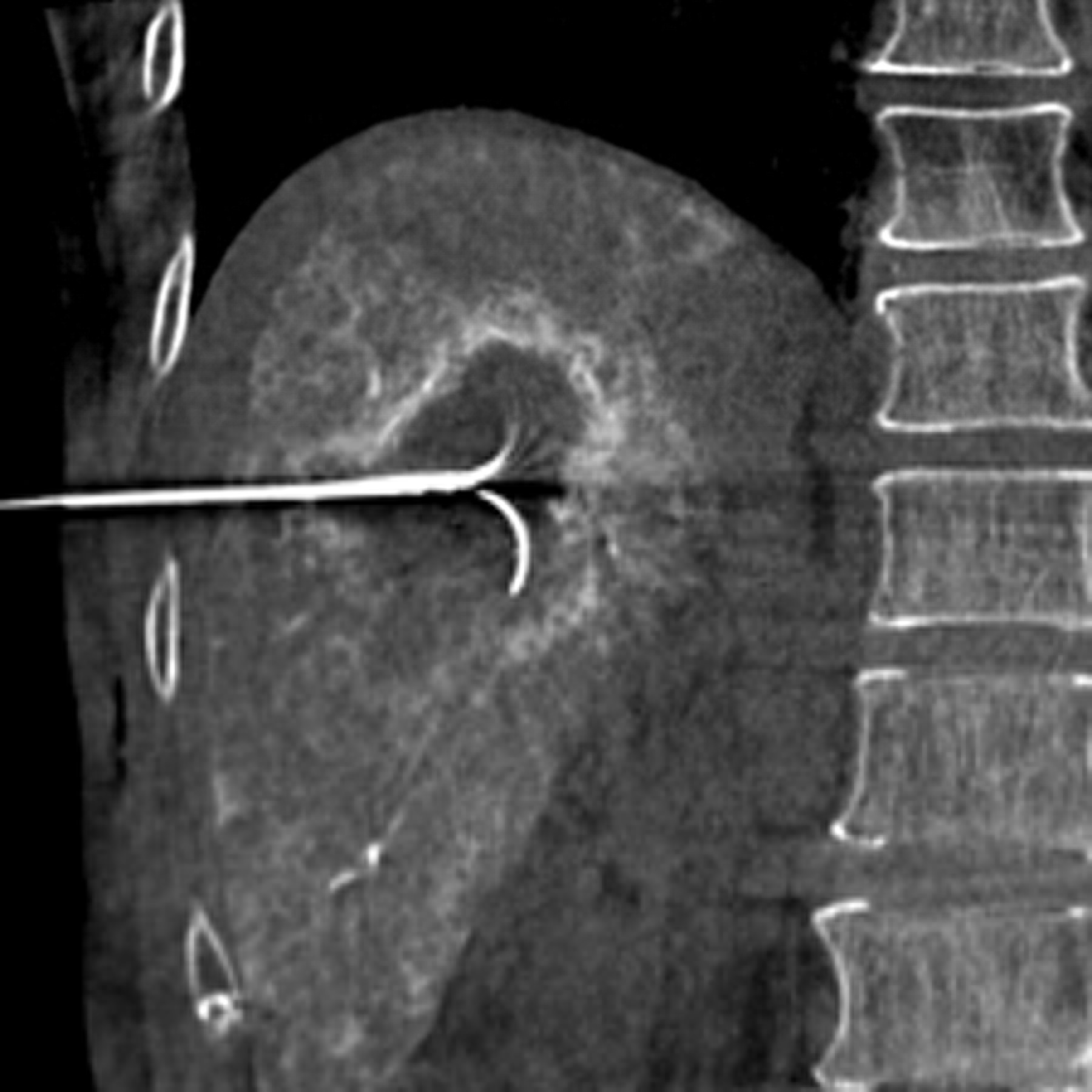
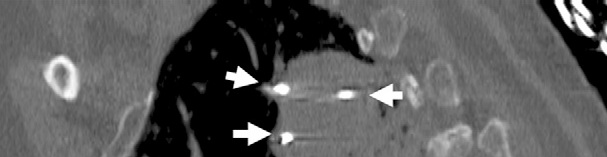
旋转平板透视的进展(或锥束CT,cone-beam CT),有类CT多平面成像和实时透视的成像的优点【52–54】。这些图像的表现在发现肿瘤方面优于标准血管造影【55】。另外其软件设计功能可用于三维血管造影数据重建,在各个方向上显示肿瘤滋养血管并因此提供经导管治疗的引导【56】。改变了日常临床介入的工作实践
除了提供类CT成像,医生还获得了典型透视下介入操作的空间。已经有X射线透视机功能的血管造影机,在肿瘤介入成像设备中具有更强大的角色【57】。 3D acquisition is routenely used
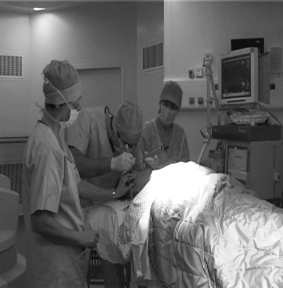
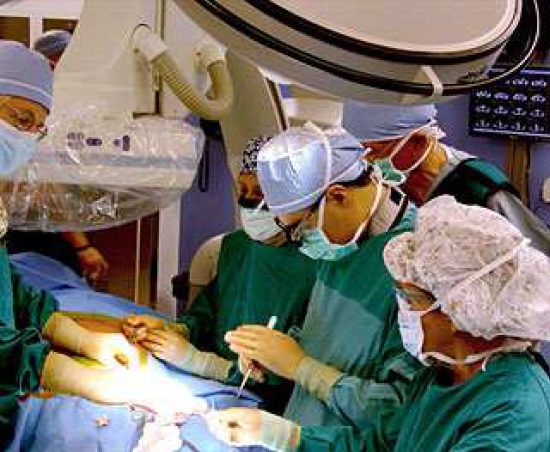
Changes in clinical practice
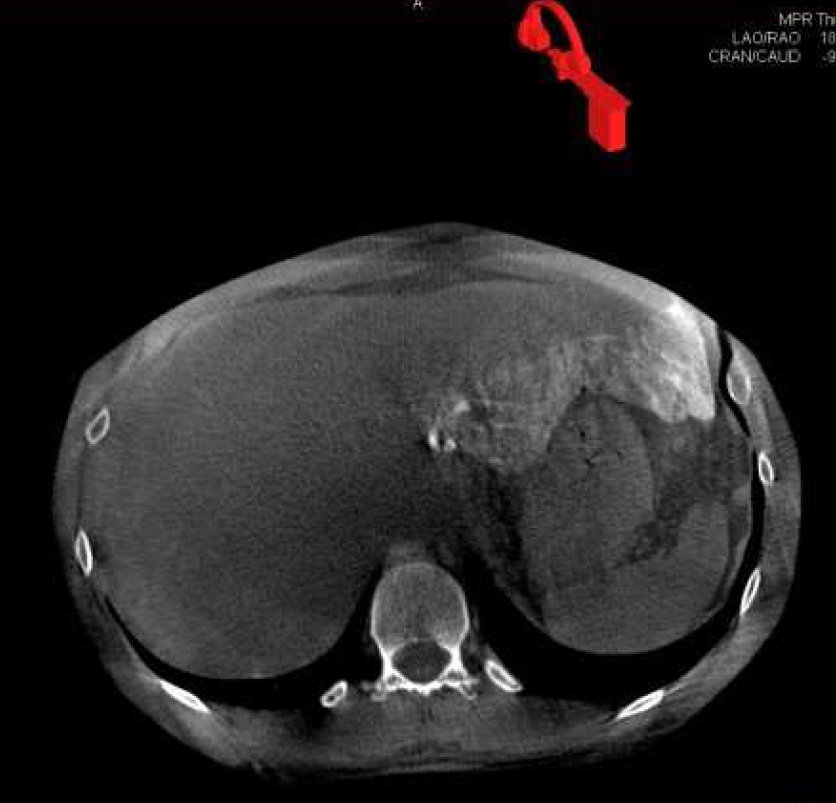
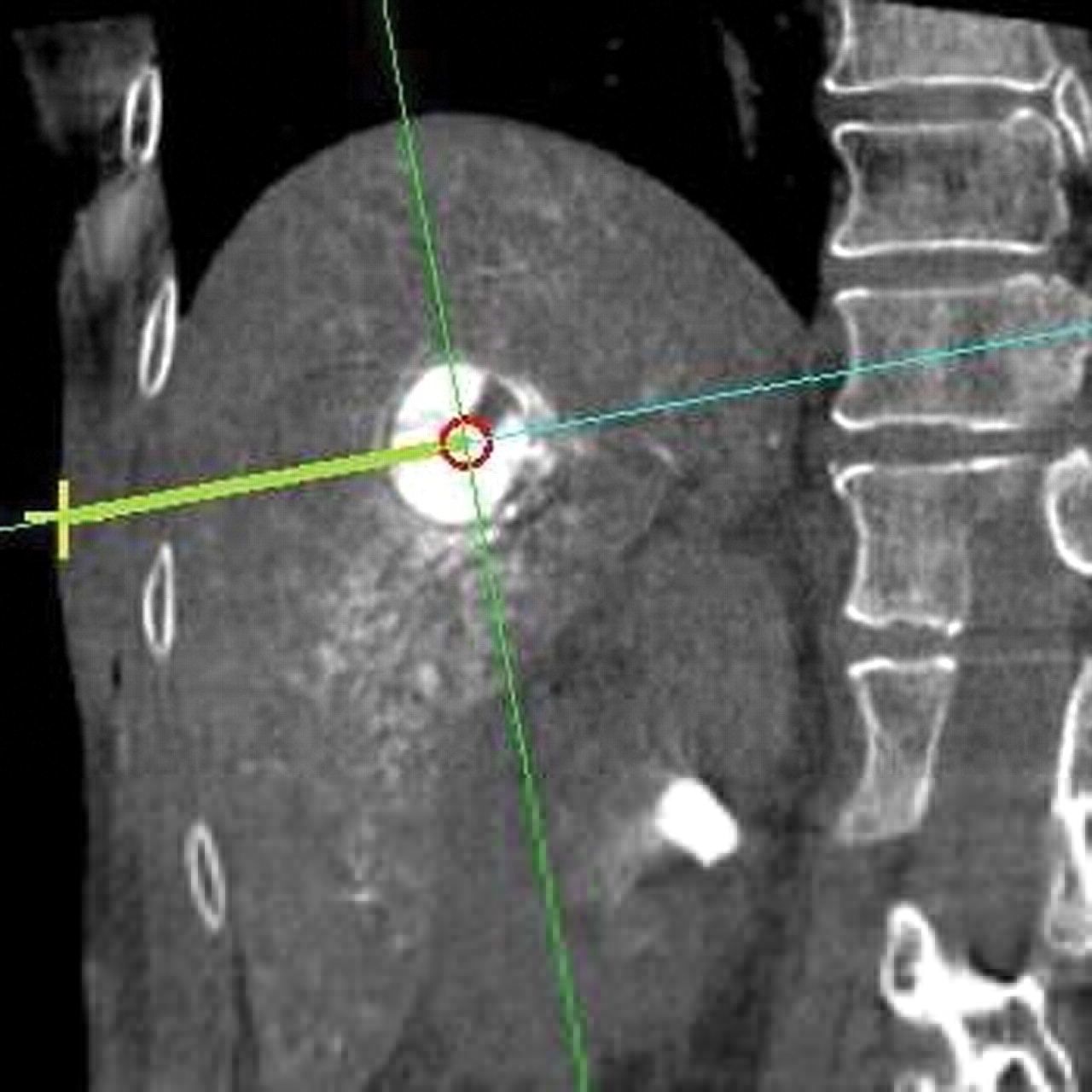
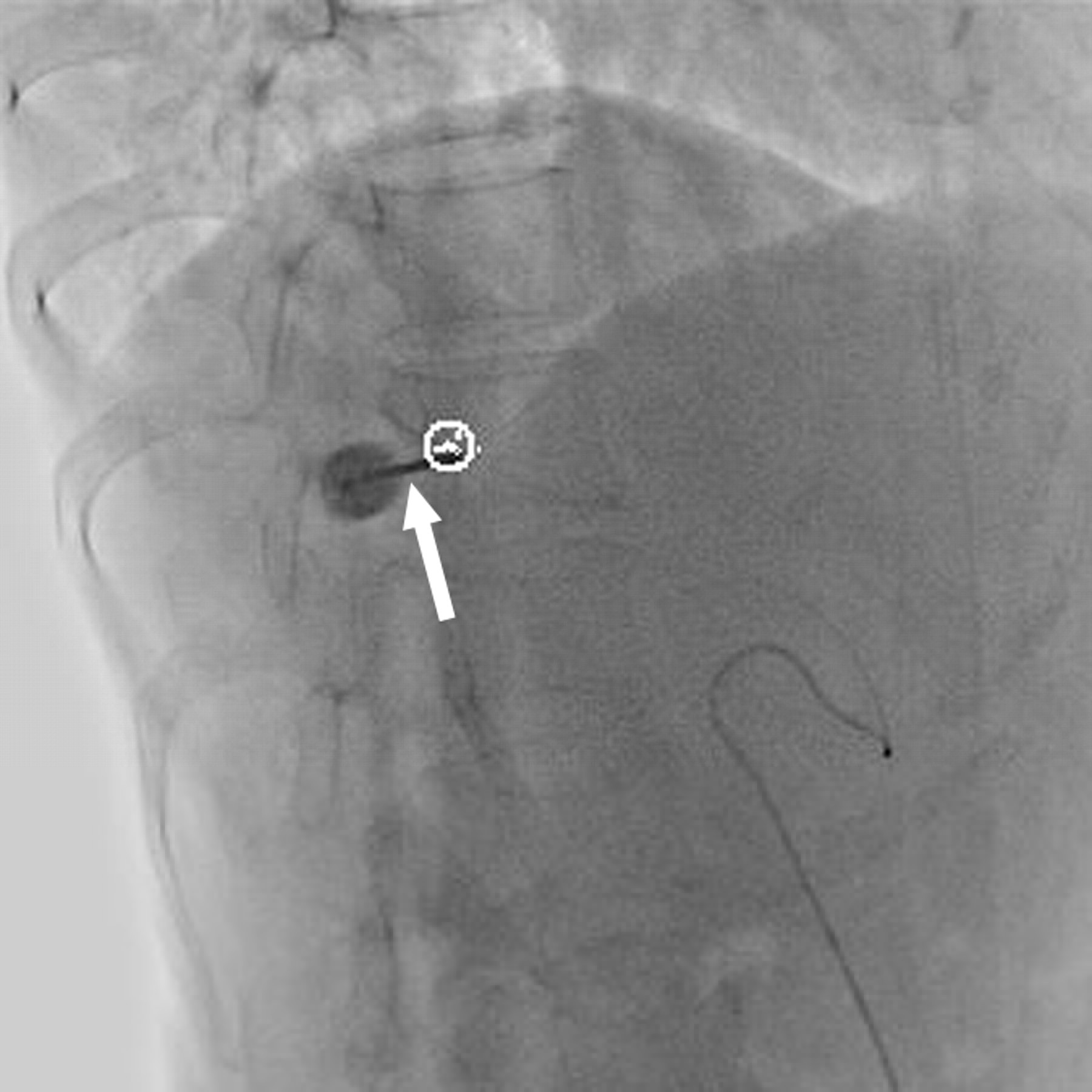
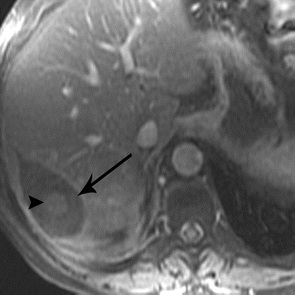
62-year-old woman with hepatocellular carcinoma in right lobe of liver.
虽然致密的结构,如骨和血管内造影剂使这些设备系统是足以实现可视化成像,在软组织分辨率和显示范围(FOV)挑战依然存。随着这一相对较新的技术的提高,许多CT引导下介入治疗可能会减少。
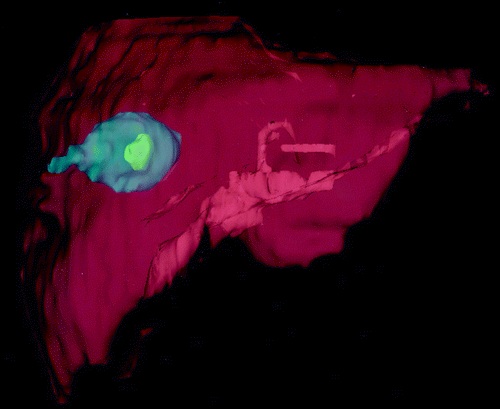
虽然CT、MRI和超声影像仍然主要在二维模式中使用,正在进行的努力是更多地应用三维影像【58】。例如,对于一个肿瘤成功地进行消融手术包括整个肿瘤的治疗,而且没有邻近结构的有害影响【59】。因此,术中肿瘤和其周围3D显示很可能改善消融的结果。早期的研究提示3D影像有助于消融电极的放置【60】。用3D影像显示的限制之一是需要时间重建影像并显示给施术者。所以快速3D影像重建的能力将有助于介入治疗【61】。
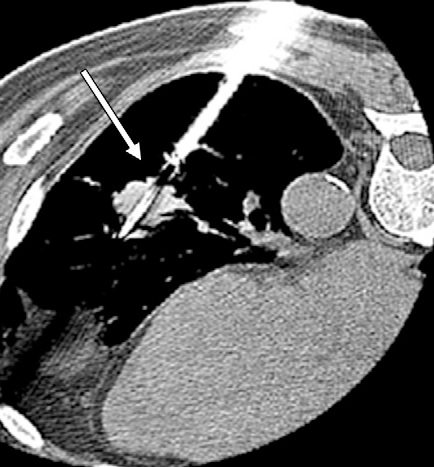
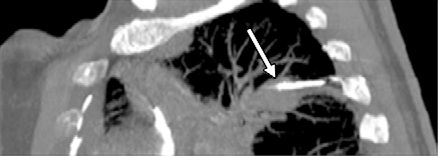
( a) Transverse CT scan shows radiofrequency ablation applicator (arrow) (Cool Tip; Valley Labs, Boulder, Colo) that appears to be in the center of 1.5-cm non–small cell lung cancer; however, (b) sagittal reconstructed CT scan shows how in reality the applicator (arrow) may be centered in the x-y dimension but not in the z dimension. The applicator is in the superior portion of the tumor, not in its center. (c, d) Different patient with three radiofrequency ablation applicators (Cool Tip) placed in a 3.5-cm non–small cell lung cancer (arrows).
(c) Sagittal and (d) transverse oblique reconstructions help determine appropriate 3D spacing of the applicators. Segmentation of structures from multiple 2D MR images to generate 3D models for volume calculations and 3D assessment of liver tumor ablations.
52. Wallace MJ . C-arm computed tomography for guiding hepatic vascular interventions . Tech Vasc Interv Radiol 2007 ; 10 ( 1 ): 79 – 86 . 53. Liapi E , Hong K , Georgiades CS , Geschwind JF . Three-dimensional rotational angiography: introduction of an adjunctive tool for
successful transarterial chemoembolization . J Vasc Interv Radiol 2005 ; 16 ( 9 ): 1241 – 1245 .
54. Beldi G , Styner M , Schindera S , Inderbitzin D , Candinas D . Intraoperative three-dimensional fl uoroscopic cholangiography . Hepatogastroenterology 2006 ; 53 ( 68 ): 157 – 159 . 55. Kakeda S , Korogi Y , Ohnari N , et al . Usefulness of cone-beam volume CT with flat panel detectors in conjunction with catheter
angiography for transcatheter arterial embolization . J Vasc Interv Radiol 2007 ; 18 ( 12 ): 1508 – 1516 .
56. Solomon SB , Thornton R , Deschamps F , et al . A treatment planning system for transcatheter hepatic therapies: pilot study . J Interv Oncol 2008 ; 1 : 12 – 18 . 57.Morimoto M , Numata K , Kondo M , et al . C-arm cone beam CT for hepatic tumor ablation under real-time 3D imaging . AJR Am J Roentgenol 2010 ; 194 ( 5 ): W452 – W454 . 58. Xu F , Mueller K . Real-time 3D computed tomographic reconstruction using commodity graphics hardware . Phys Med Biol 2007 ;
52 ( 12 ): 3405 – 3419 .
59. Silverman SG , Sun MRM , Tuncali K , et al . Three-dimensional assessment of MRI-guided percutaneous cryotherapy of liver metastases . AJR Am J Roentgenol 2004 ; 183 ( 3 ): 707 – 712 . 60. Antoch G , Kuehl H , Vogt FM , Debatin JF , Stattaus J . Value of CT volume imaging for optimal placement of radiofrequency ablation
probes in liver lesions . J Vasc Interv Radiol 2002 ; 13 ( 11 ): 1155 – 1161 .
61. Chin JL , Downey DB , Onik G , Fenster A . Three-dimensional prostate ultrasound and its application to cryosurgery . Tech Urol 1996 ; 2 ( 4 ): 187 – 193 . |