作为介入标靶影像方式之一,CT透视是在介入手术房间内实时显示操作过程。CT透视允许肿瘤介入医师在房间里实时观察操作过程。传统需要操作医生每次操作后(如穿刺针前进后),在CT扫描房间里外移动。CT透视技术的缺点是辐射剂量的增加,缺乏三维重建【30】。试图减少在CT透视时的辐射暴露,可通过降低每幅图像的采集剂量,实现角光束调制,并提供了介入器械臂【31–33】。
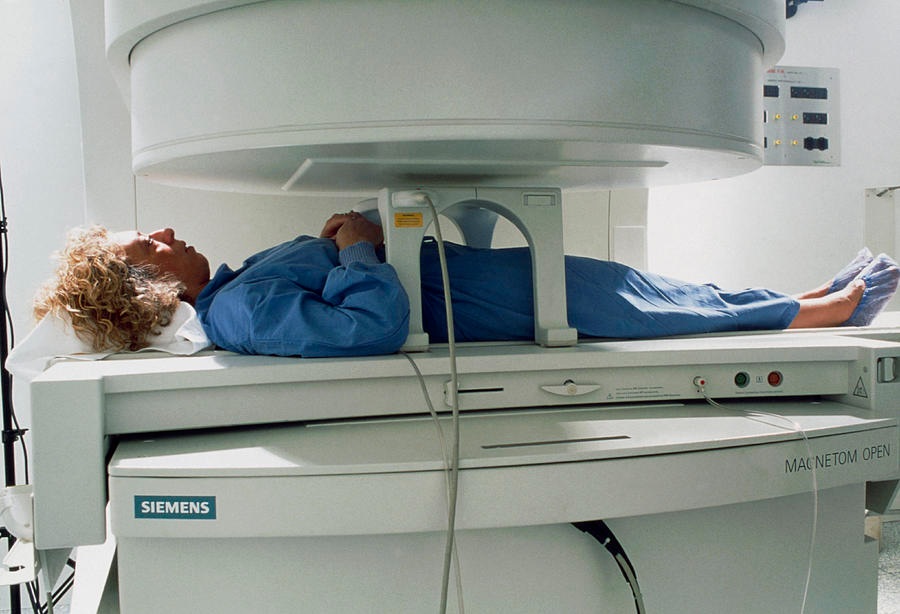
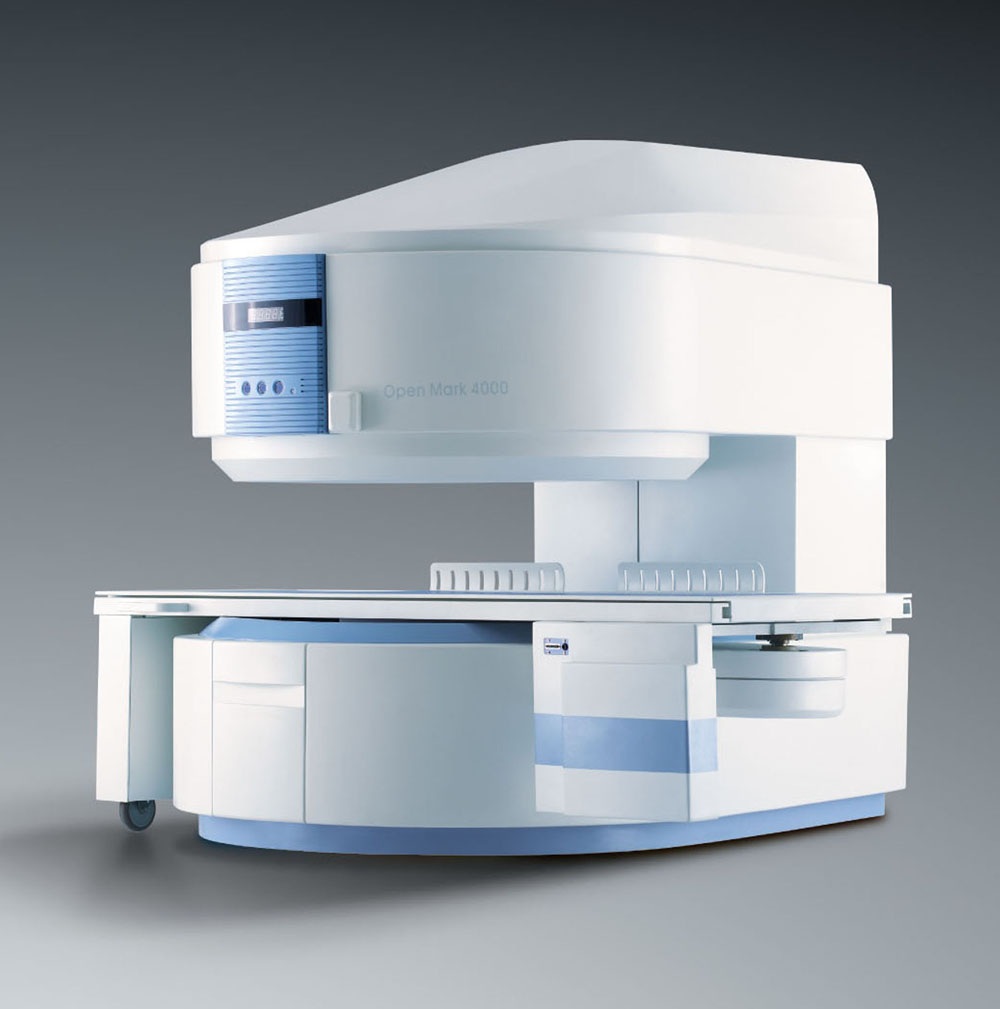
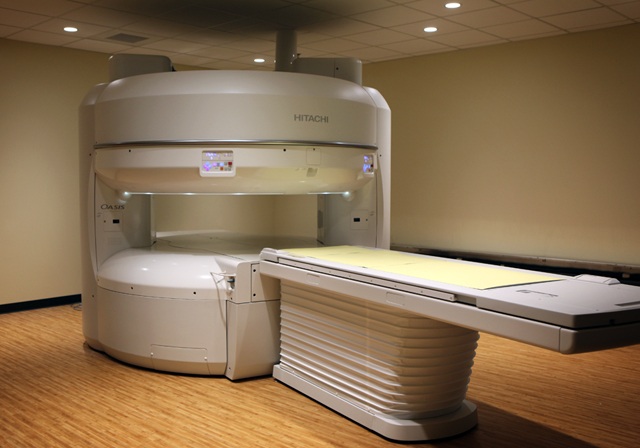
利用MRI透视技术,磁共振成像也提供了实时、多平面成像而没有电离辐射【34】。磁共振成像使肿瘤介入治疗可视化【35】,和提供消融热监测【36–42】。然而,封闭设计的狭小的空间,低或中等场强磁共振成像系统对医生和病人都是一个限制;已部分地克服这些缺陷的新的MRI系统正在和已经开发中【43,44】。大口径(70厘米),高磁场强度的磁体(1.5T)已被用来提供更好的病人进入空间和更高的图像质量。比这些宽孔磁铁,老“双炸圈饼(double-doughnut)”和开放的磁体磁场强度较低。新磁铁适合介入治疗的应用【45,46】。
MRI引导下的介入治疗有许多的障碍(如MR不兼容的仪器)已经得到解决,但有些障碍仍然存在,例如,在扫描过程中产生的噪声对介入治疗是有害的,特别是新一代的3T系统【47,48】。其他的挑战也仍然存在,如射频消融干扰磁共振成像的电噪声【49】。器械可视化问题仍然存在,是因为太多伪影几乎谈不上清晰性【50、51】。此外,床位屋内控制和图像序列将有助于优化MRI的肿瘤介入手术。
30. de Mey J , Op de Beeck B , Meysman M , et al . Real time CT-fluoroscopy: diagnostic and therapeutic applications . Eur J Radiol 2000 ; 34 ( 1 ): 32 – 40 . 31. Yamao Y , Yamakado K , Takaki H , et al . Optimal scan parameters for CT fluoroscopy in lung interventional radiologic procedures: relationship between radiation dose and image quality . Radiology 2010 ; 255 ( 1 ): 233 – 241 . 32. Hohl C , Suess C , Wildberger JE , et al . Dose reduction during CT fluoroscopy: phantom study of angular beam modulation . Radiology 2008 ; 246 ( 2 ): 519 – 525 . 33. Irie T , Kajitani M , Itai Y . CT fluoroscopy guided intervention: marked reduction of scattered radiation dose to the physician’s hand by use of a lead plate and an improved I-I device . J Vasc Interv Radiol 2001 ; 12 ( 12 ) : 1417 – 1421 . 34. Yutzy SR , Duerk JL . Pulse sequences and system interfaces for interventional and real-time MRI . J Magn Reson Imaging 2008 ; 27 ( 2 ): 267 – 275 . 35. Saybasili H , Faranesh AZ , Saikus CE ,Ozturk C , Lederman RJ , Guttman MA .Interventional MRI using multiple 3D angiography
roadmaps with real-time imaging .J Magn Reson Imaging 2010 ; 31 ( 4 ): 1015 – 1019 .
36. Puls R , Langner S , Rosenberg C , et al .Laser ablation of liver metastases from colorectal cancer with MR thermometry: 5-year survival . J Vasc Interv Radiol 2009 ; 20 ( 2 ): 225 – 234 . 37. Pech M , Wieners G , Freund T , et al . MR guided interstitial laser thermotherapy of colorectal liver metastases: effi ciency, safety
and patient survival . Eur J Med Res 2007 ; 12 ( 4 ): 161 – 168 .
38. Mougenot C , Quesson B , de Senneville BD , et al . Three-dimensional spatial and temporal temperature control with MR thermometry guided focused ultrasound (MRgHIFU) . Magn Reson Med 2009 ; 61 ( 3 ): 603 – 614 . 39. Silverman SG , Tuncali K , Morrison PR . MR imaging-guided percutaneous tumor ablation . Acad Radiol 2005 ; 12 ( 9 ): 1100 – 1109 . 40. Silverman SG , Tuncali K , Adams DF , et al . MR imaging-guided percutaneous cryotherapy of liver tumors: initial experience . Radiology
2000 ; 217 ( 3 ): 657 – 664 .
41. Gedroyc WM . Magnetic resonance guidance of thermal ablation . Top Magn Reson Imaging 2005 ; 16 ( 5 ): 339 – 353 . 42. Roujol S , Ries M , Quesson B , Moonen C , Denis de Senneville B . Real-time MR thermometry and dosimetry for interventional
guidance on abdominal organs . Magn Reson Med 2010 ; 63 ( 4 ): 1080 – 1087 .
43. Morrison PR , Silverman SG , Tuncali KT , Tatli S . MRI-guided cryotherapy . J Magn Reson Imaging 2008 ; 27 ( 2 ): 410 – 420 . 44. Boss A , Clasen S , Kuczyk M , et al . Magnetic resonance-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of renal cell carcinomas:
a pilot clinical study . Invest Radiol 2005 ; 40 ( 9 ): 583 – 590 .
45.Fritz J , Clasen S , Boss A , et al . Real-time MR fl uoroscopy-navigated lumbar facet joint injections: feasibility and technical properties
. Eur Radiol 2008 ; 18 ( 7 ): 1513 – 1518 .
|