定义:胰腺急性炎症的情况,由异常活性的胰酶触发,并释放各种炎性介质。 历史:
Claude Bernard 在1856年认为胆道胆汁返流到胰腺是引起胰腺炎的诱因。
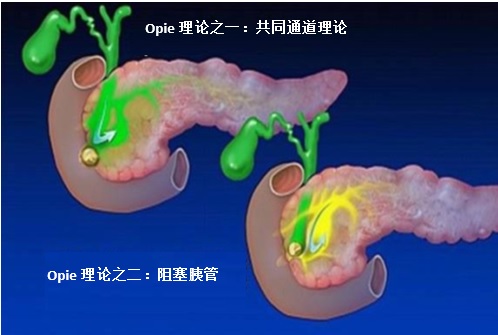
1901,Eugene Opie提出,胆结石迁移到胆总管是急性胰腺炎的主要原因。
从那时起,许多其他原因的胰腺炎被发现。本栏目是回顾急性胰腺炎的进展,尤其是在介入放射学方面的进展【9】。 急性胰腺炎的发病率在过去的二十年中有所增加。目前急性胰腺炎每年占美国住院病人20万人以上。这种增长也见于欧洲。在80%的患者中,急性胰腺炎是轻度的,经治疗并不产生不严重并发症。多达20%,急性胰腺炎并发严重并发症甚至导致死亡【9】。 有关急性胰腺炎的名词(-摘自亚特兰大急性胰腺炎2012共识)
急性胰腺炎 Acute Pancreatitis, AP
轻度急性胰腺炎 Mild Acute Pancreatitis,MAP
中度急性胰腺炎 Moderately Severe Acute Pancreatitis,MSAP
重度急性胰腺炎 Severe Acute Pancreatitis,SAP
间质水肿胰腺炎 Interstitial (o)edematous pancreatitis,IEP
坏死性胰腺炎 Necrotising pancreatitis,NP
感染性胰腺坏死 Infected pancreatitis necrosis,IPN
诊断AP 需要以下3 个特点中的2 个:
(1) 符合AP腹痛 特征(急性发作的持续性的、严重的上腹部痛,常放射到背部); (2) 血清脂肪酶活性(或淀粉酶活性) 至少大于正常上限3 倍; (3)增强CT 发现胰腺肿大、渗出或坏死等AP 特征性改变,少数情况使用磁共振成像(MRI) 或腹部超声检查。 在1992美国亚特兰大根据胰腺炎的各种表现建立了一个普遍适用的急性胰腺炎分类系统和诊治规范,被称为亚特兰大共识【1】。此后它作为急性胰腺炎分类诊治的基石引领急性胰腺炎治疗20多年。该共识的目的是便于理解消化科、病理医生、放射科和外科医生临床发现的相关性,特别有助于急性胰腺炎病程各种流体积聚的评估和治疗。它定义了急性胰腺炎作为胰腺与其他局部组织和远程器官系统的变量参的一种急性炎症过程。轻度胰腺炎被描述为以最小的器官功能障碍和术后恢复。重症胰腺炎定义为器官衰竭和/或局部如急性假性囊肿,胰腺坏死的并发症,或胰腺脓肿(尽管被2012年的共识所去除)【2】。 由于微创技术、疾病研究和影像学的进展1992年亚特兰大共识不断遭到质疑【3】,历经2007年以来对国际胰腺炎工作组修改草案【4】的一系列网络形式的3轮讨论和修改【4~7】。最终形成了急性胰腺炎亚特兰大2012年共识【8】。
新共识提倡早期器官支持、营养优化的原则,理想情况下,随后的微创治疗(minimally invasion intervention) 1. Bradley EL. A clinically based classification system for acute pancreatitis. Summary of the International Symposium on Acute Pancreatitis, Atlanta, Ga, September 11 through 13, 1992. Arch Surg 1993;128(5):586–590. 2. Bollen TL, Besselink MG, van Santvoort HC, Gooszen HG, van Leeuwen MS. Toward an update of the Atlanta classification on acute pancreatitis: review of new and abandoned terms. Pancreas 2007;35(2):107–113 3. 1. Bollen TL, van Santvoort HC, Besselink MG, et al. The Atlanta Classification of acute pancreatitis revisited[J]. Br J Surg, 2008,95 (1): 6-21 4. Group APCW. Revision of the Atlanta classification of acute pancreatitis [DB/OL].http://pancreasclub.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/11/AtlantaClassification pdf 2008. (http://pancreasclub.com/=胰腺俱乐部) 5. Brun A,Agarwal N,Pitchumoni CS. Fluid collections in and around the pancreas in acute pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2011,45(7) : 614 - 625. 6. Sheu Y,Furlan A, Almusa O, et al. The revised Atlanta classification for acute pancreatitis: a CT imaging guide for Radiologists[J]. Emerg Radiol,2011,19( 3) : 237-243. 7. Thoeni RF. The revised atlanta classification of acute pancreatitis: its importance for the radiologist and its effect on treatment[J],Radiology, 2012,262( 3) : 751-764. 8. Banks PA,Bollen TL,Dervenis C, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis-2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus[J]. Gut,2013,62( 1) : 102 -111. 9. Ferreira Ade F, Bartelega JA, Urbano HC, de Souza IK .Acute pancreatitis gravity predictive factors: which and when to use them? Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2015 Jul-Sep;28(3):207-11. [Article in English, Portuguese] doi: 10.1590/S0102-67202015000300016. |