产后出血(PPH)的危险因素取决于出血的病因。
子宫弛缓的危险因素包括多产妇(high maternal parity)、绒毛膜羊膜炎、长期使用催产素、全身麻醉,以及导致子宫扩张增加的情况,如多胎妊娠、羊水过多、胎儿巨大儿和子宫肌瘤。
Risk factors that can lead to uterine inversion include excessive umbilical cord traction, short umbilical cord, and fundal implantation of the placenta.
可导致子宫倒置的危险因素包括脐带过度牵引、脐带短和胎盘眼底植入。
Genital tract trauma risk factors include operative vaginal delivery and precipitous delivery.
生殖道创伤的危险因素包括手术阴道分娩和产程过短。
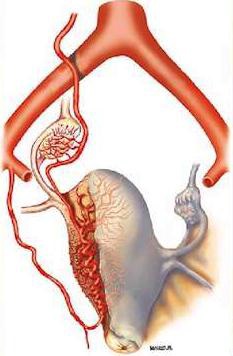
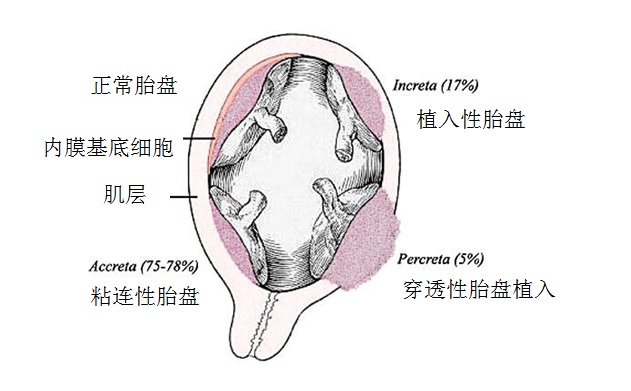
Retained placenta and abnormal placentation are more common if an incomplete placenta is noted at delivery, a succenturiate lobe of the placenta is present, or if the patient has a history of previous uterine surgery.
如果在分娩时发现胎盘不完整,胎盘存在副胎盘,或患者有子宫手术史,保留胎盘和异常胎盘形成更常见。
Coagulation abnormalities are more common in patients presenting with fetal death in utero, placental abruption, sepsis, disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC), and in those with a history of an inherited coagulation defect.
凝血异常在子宫内胎儿死亡、胎盘早剥、脓毒症、弥散性血管内凝血病障碍(DIC)和有遗传性凝血缺陷病史的患者中更为常见。
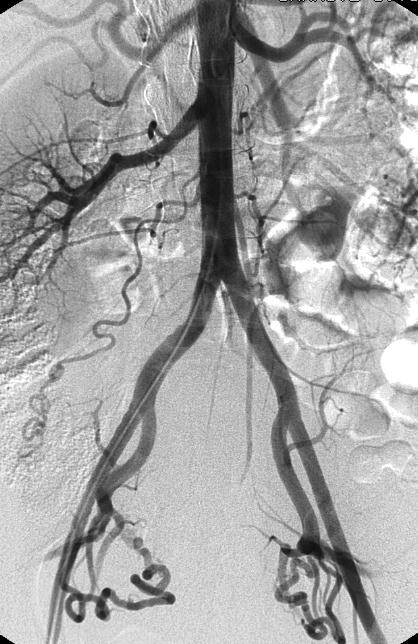
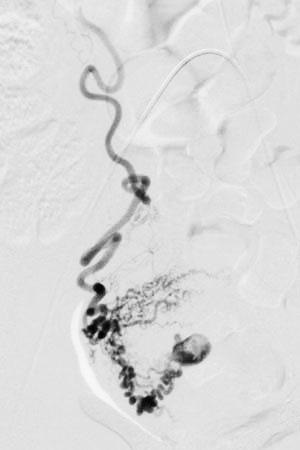
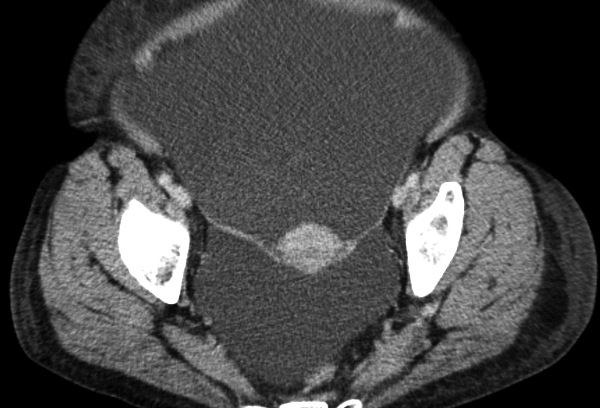
在国际上有一个被称为“产科出血工具包2.0(OB Hemorrhage Toolkit V2.0)”,它的出血工作组开发了改善产科出血反应工具包,以帮助产科医生、临床工作人员、医院和保健机构在其设施内制定方法,及时发现和有组织的快速应对出血。 产科出血工具包2.0指出: 分娩时出血、有PPH史、红细胞压积小于30%、出血倾向或凝血功能差、胎盘病态附着或分娩时有低血压或心动过速的患者,入院时为PPH的高风险
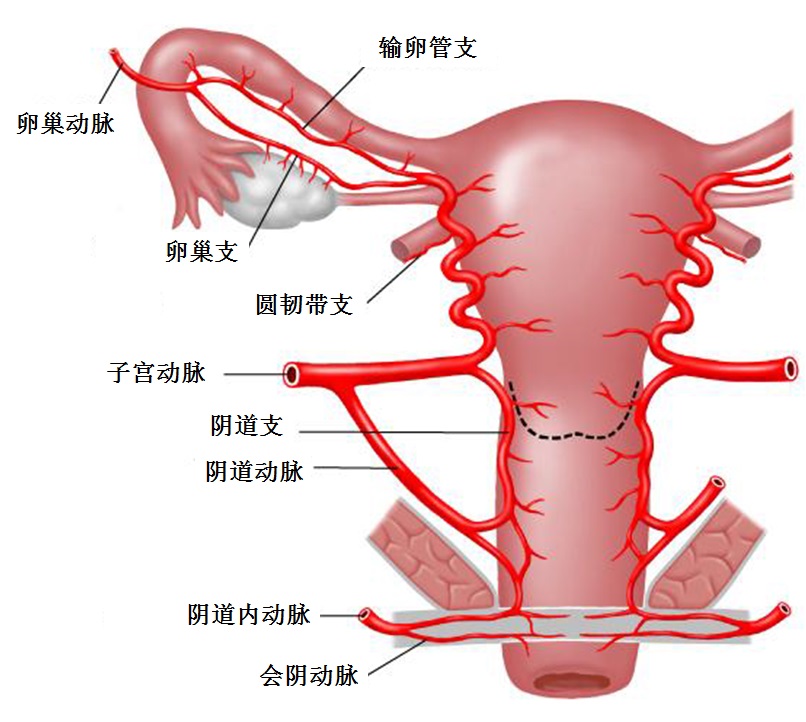
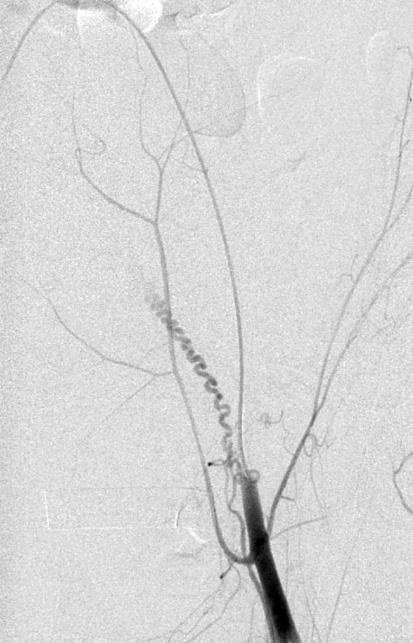
Vascular supply of the uterus
子宫的侧支循环
圆韧带
 |