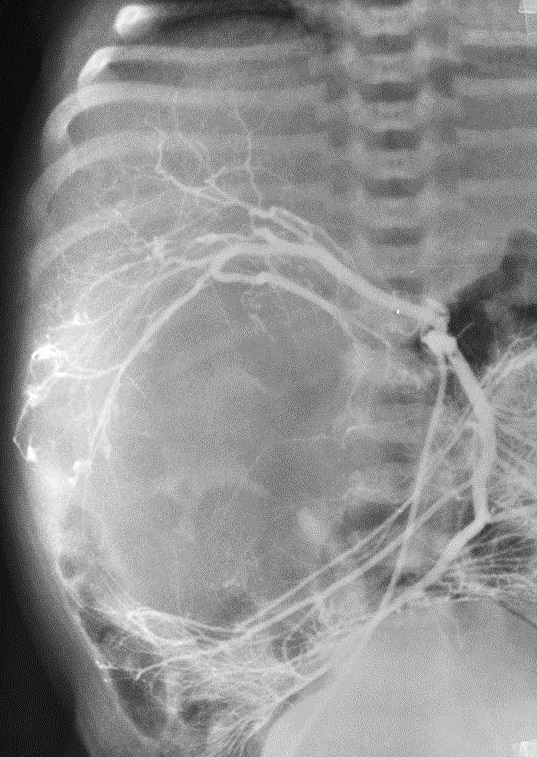
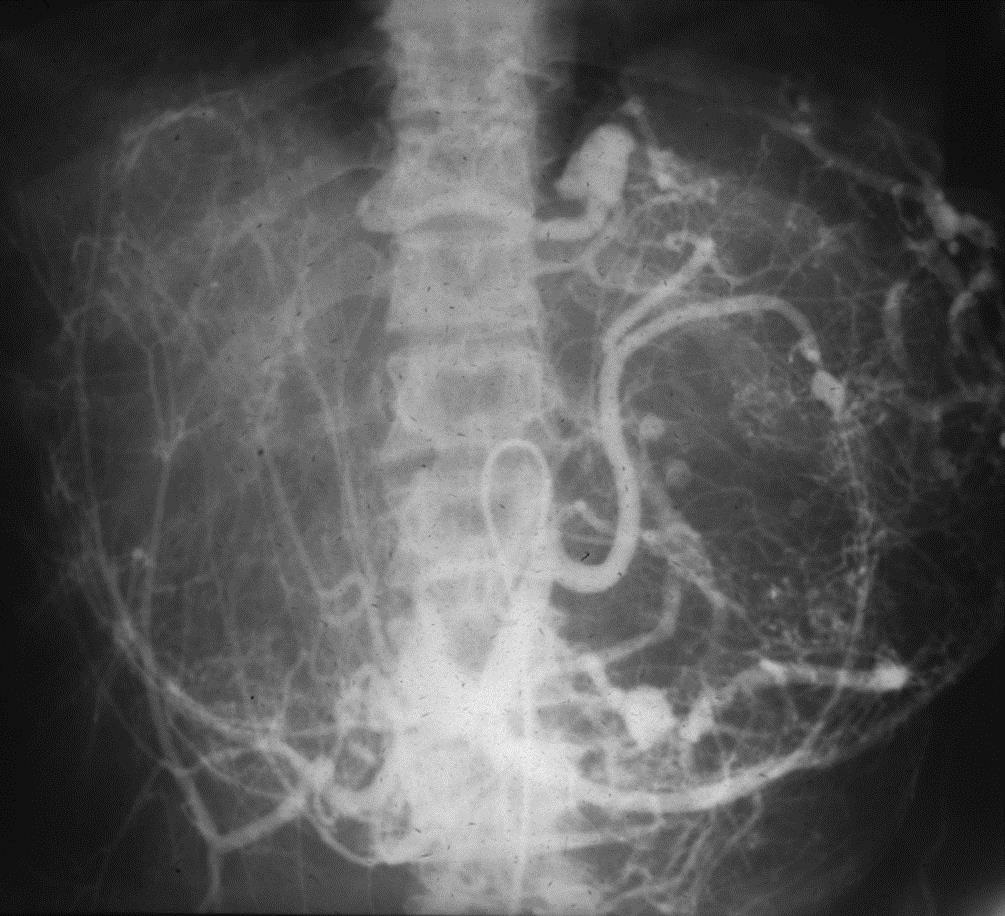
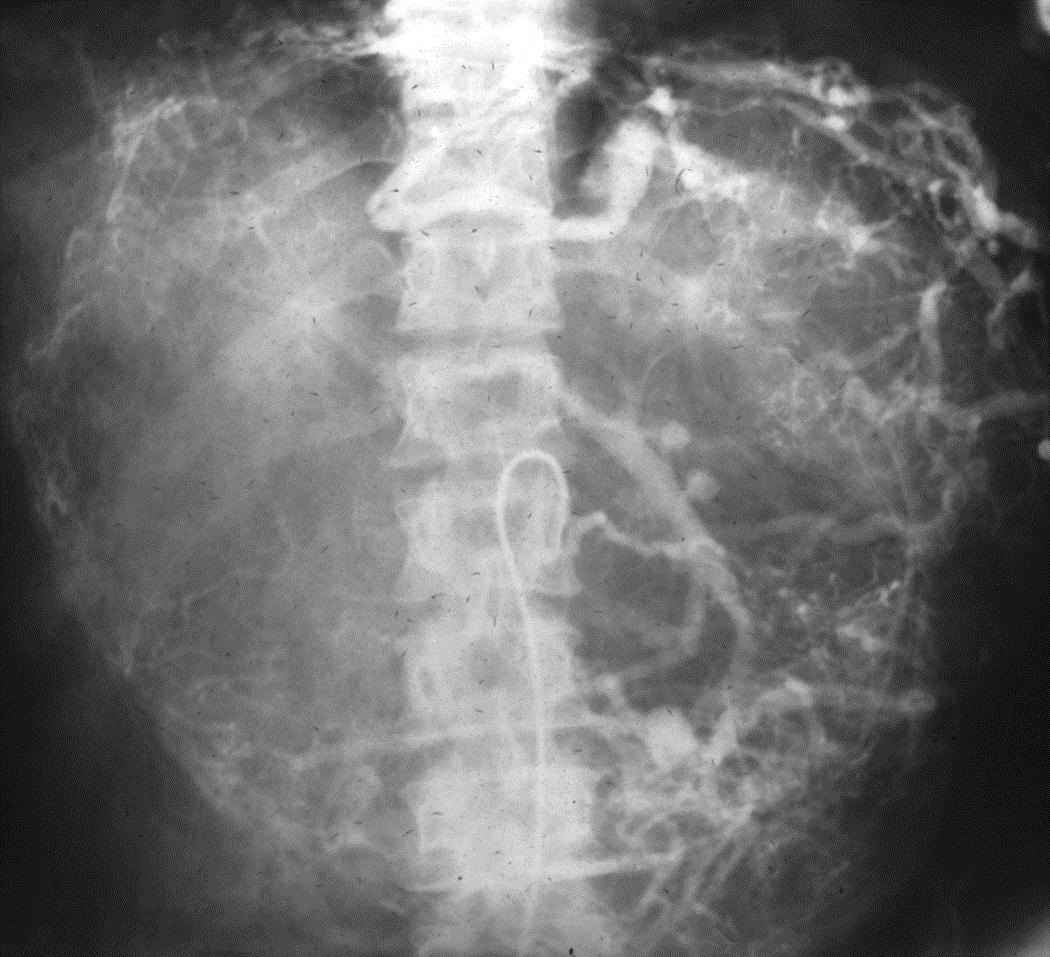
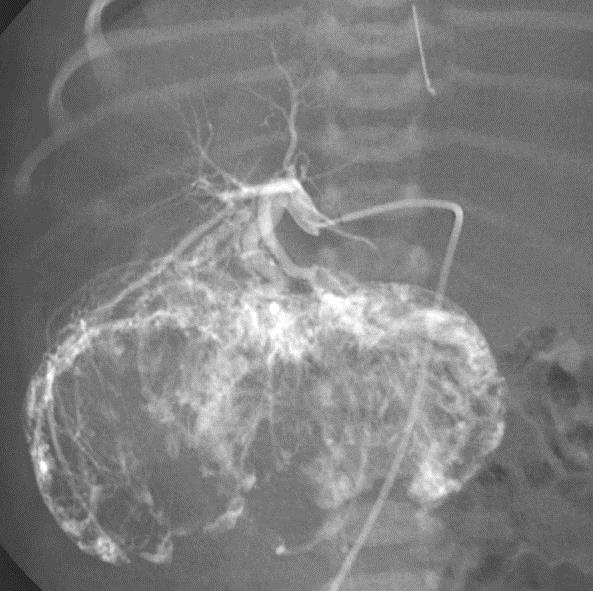
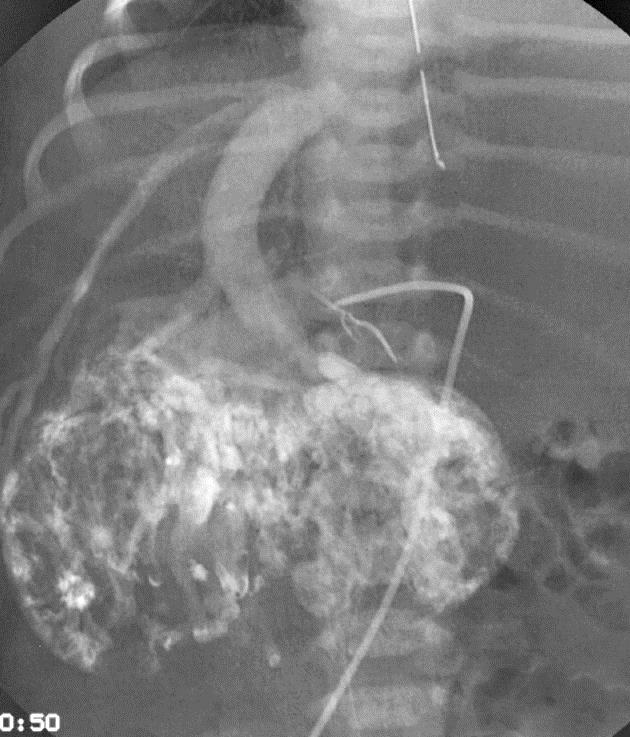
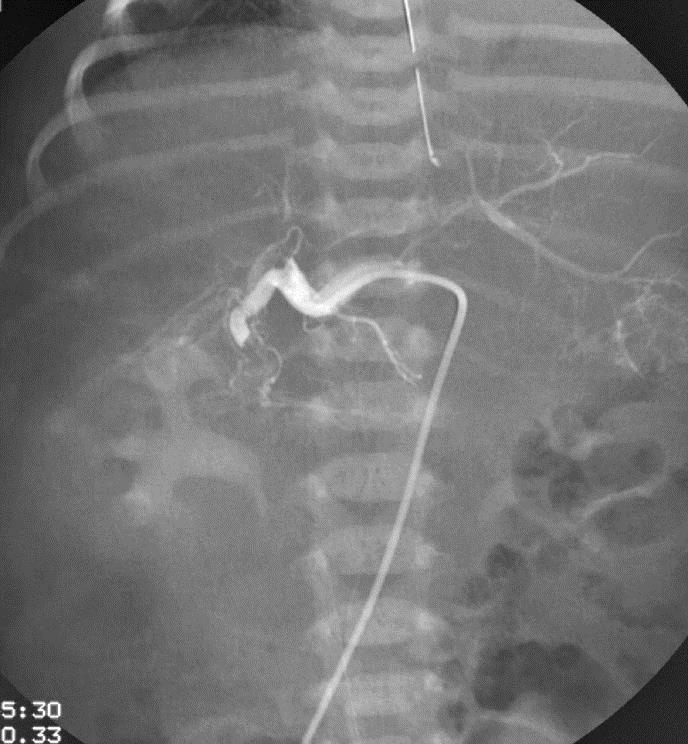
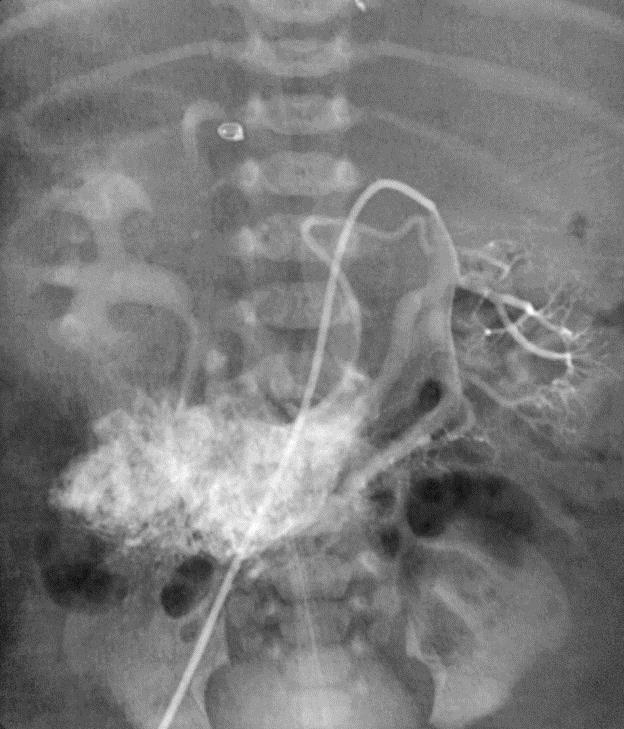
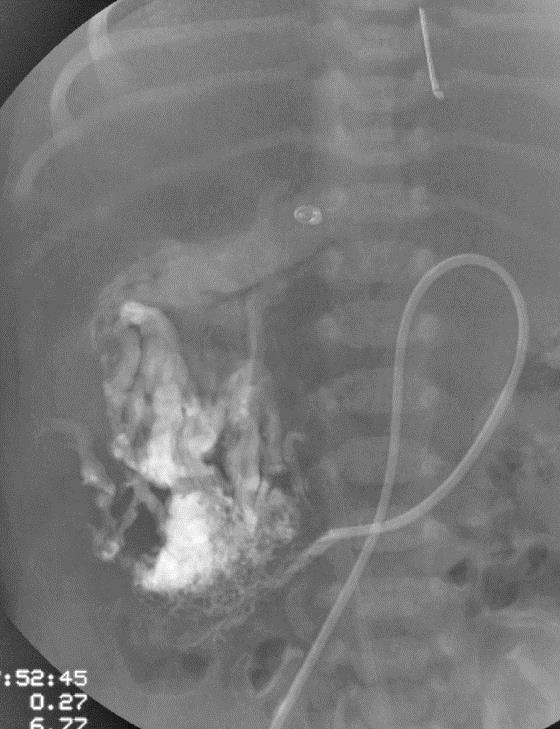
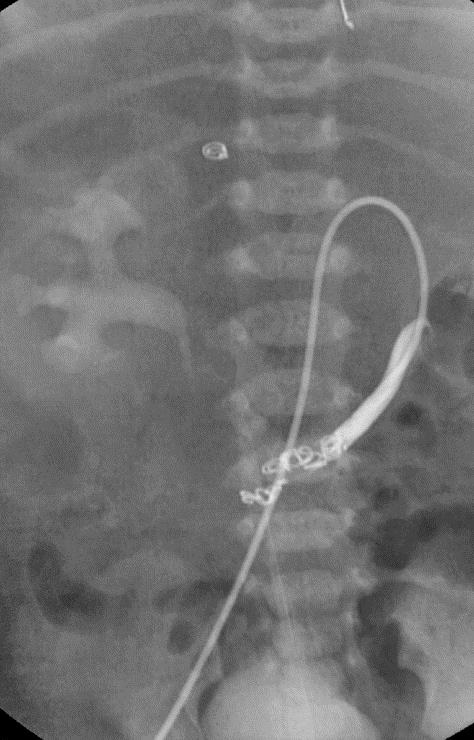
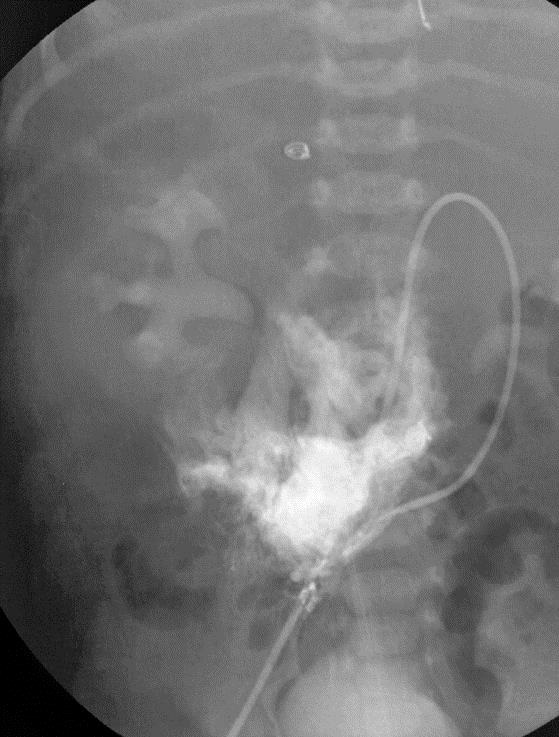
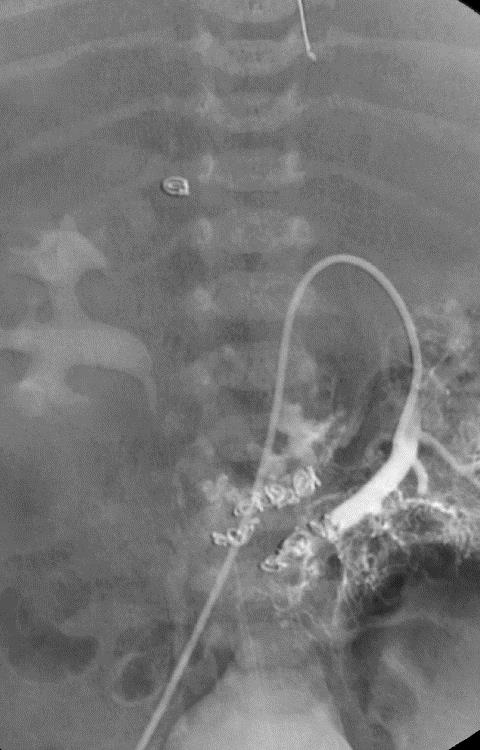
小儿肝血管内皮瘤(Infantile hepatic hemangioendothelioma) 婴儿型肝脏血管内皮细胞瘤是一种毛细血管性血管瘤,大多数见于6个月以内的婴儿,女孩多见,男女之比1:2【1,2】。该疾病小儿最常见的血管肿瘤,出生后头几个月快速生长,可自发性退化。血管造影表现包括没有直接分流的证据,可以发现造影剂延迟池样聚集(delayed pooling);没有直接分流的高血流量结节的死亡率可达50%。血管造影表现还包括直接动静脉分流和直接门静脉-肝静脉分流,以及两者同时存在【1】。 Hemangioendothelioma Type 1
Hemangioendothelioma Type 2
在自发性退化之前可能的并发症包括,高心输出量导致的心力衰竭,弥漫性血管内凝血,腹部间隔综合症,致命性出血,门静脉高压和消化道出血。 治疗的选择包括激素、干扰素、栓塞、外科切除和肝移植。
1. Parker BR. The hepatobiliary system. In: Silverman FN, Kuhn JP. Caffey’s pediatric x-ray diagnosis: an integrated imaging approach. 9th ed. St Louis, Mo: Mosby, 1993.915-969
2. Buonomo C, Taylor GA, Share JC, Kirks DR. Abnormalities of the hepatobiliary system. In: Kirks DR, Griscom NT. Practical pediatric imaging: diagnostic radiology of infants and children. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott-Raven, 1998. 954-979 3. Kassarjian A, Dubois J, Burrows PE. Angiographic classification of hepatic hemangiomas in infants. Radiology. 2002 Mar;222(3):693-8. |