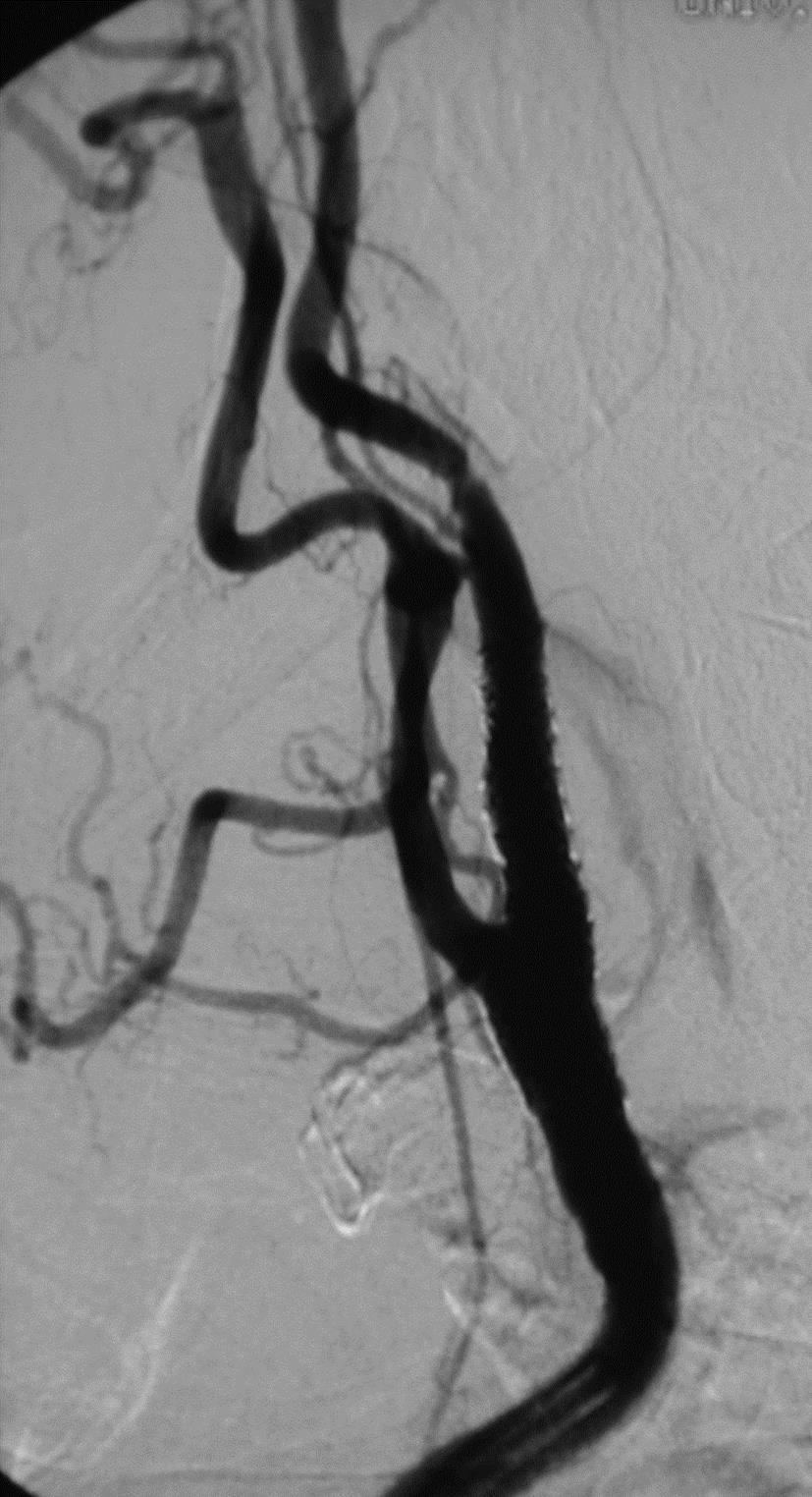
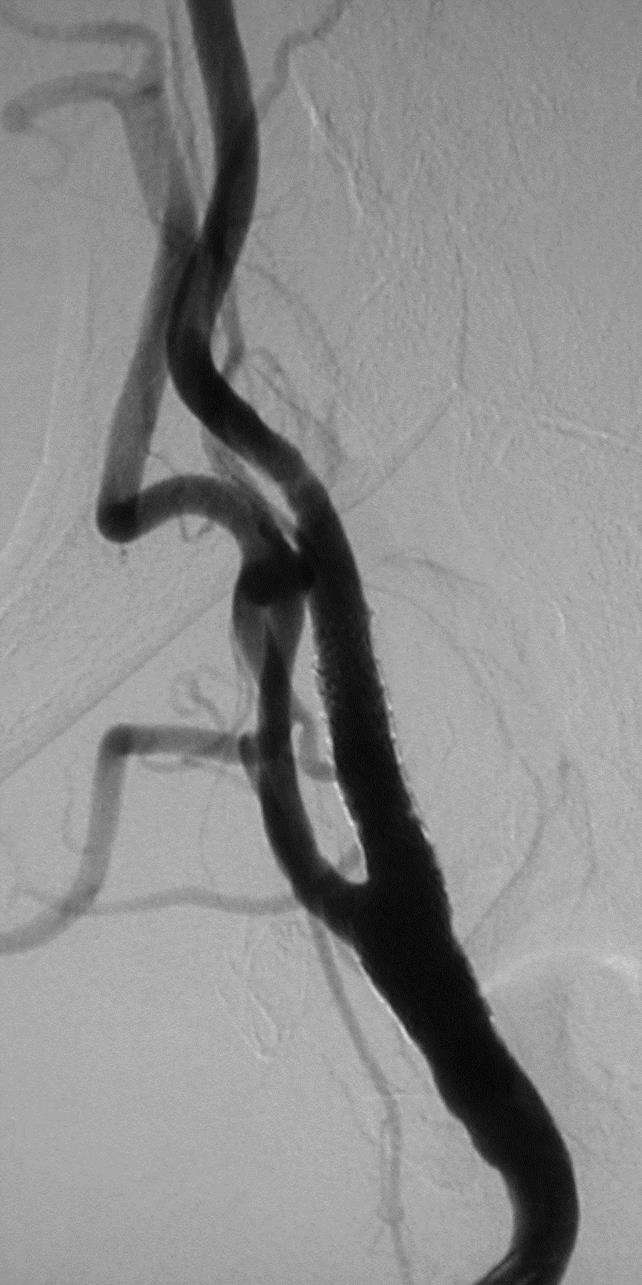
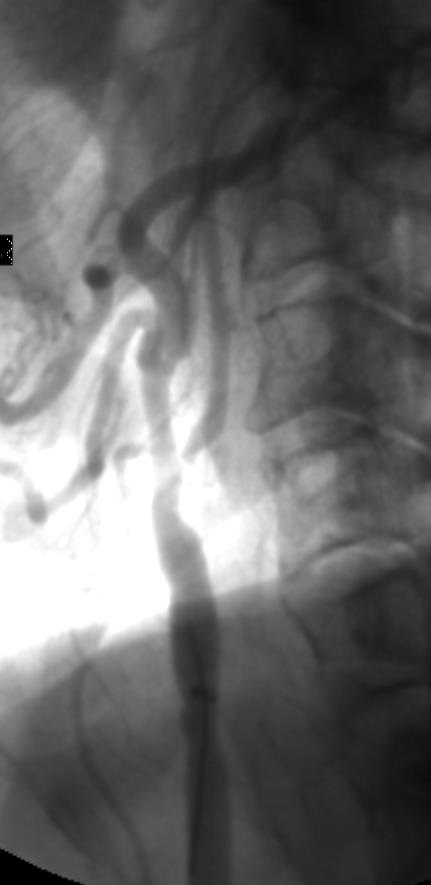
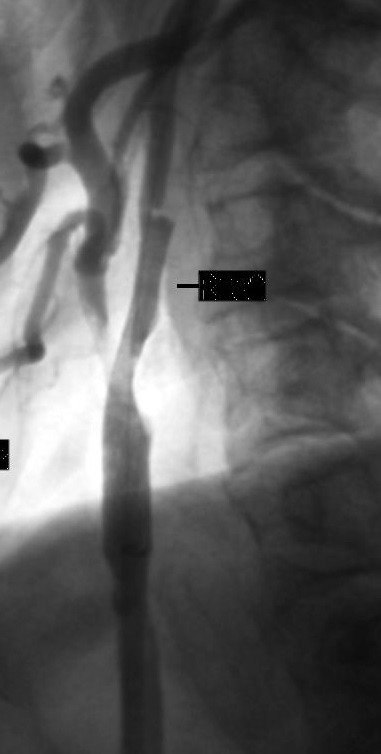
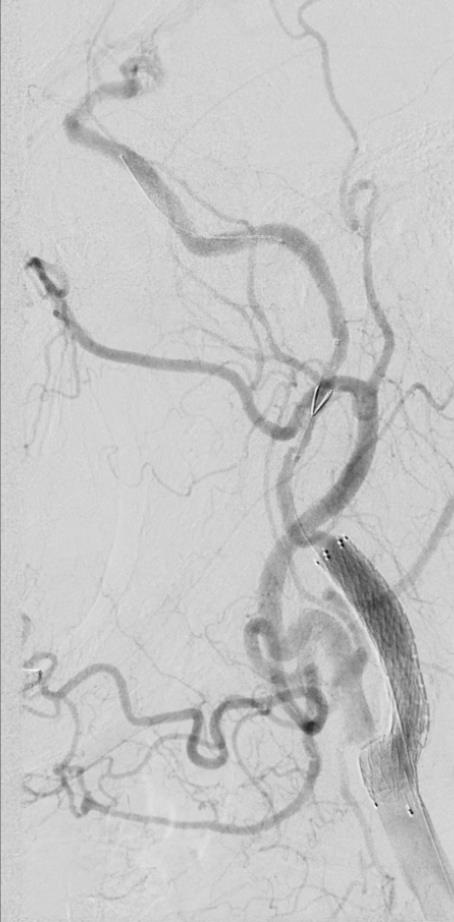
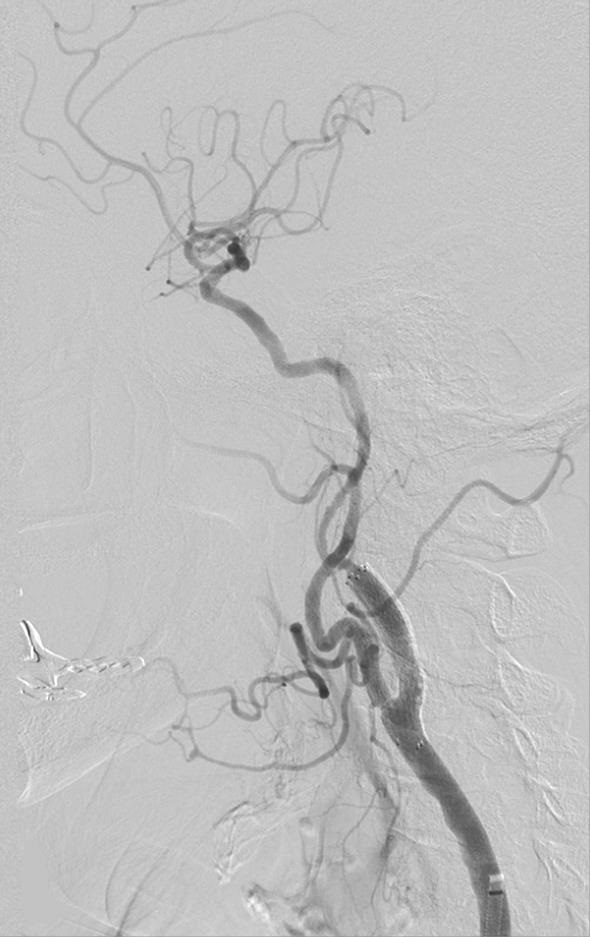
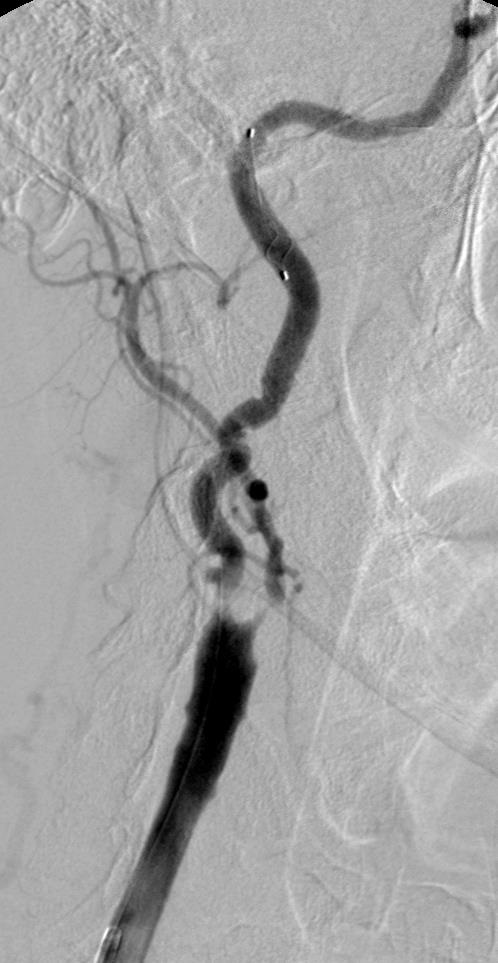
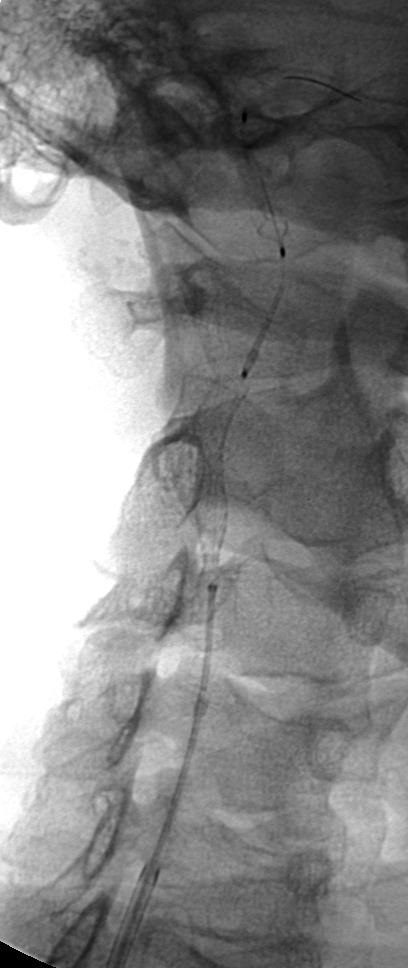
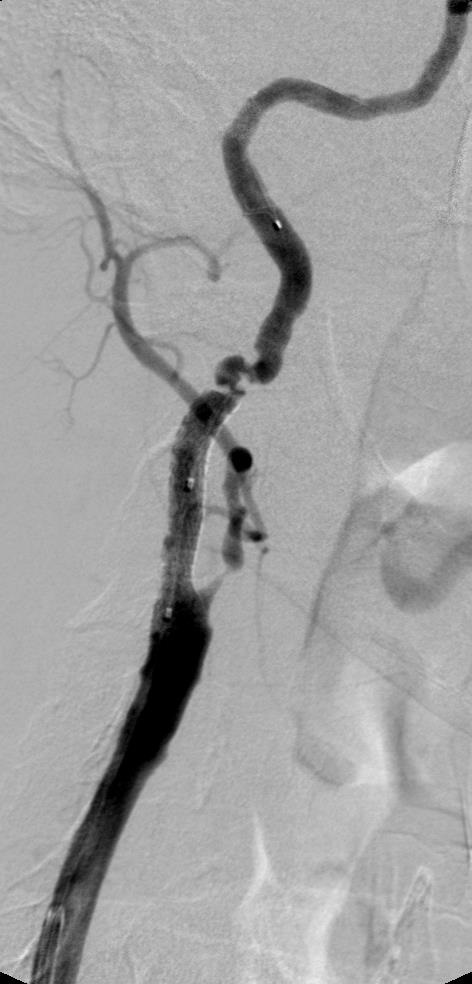
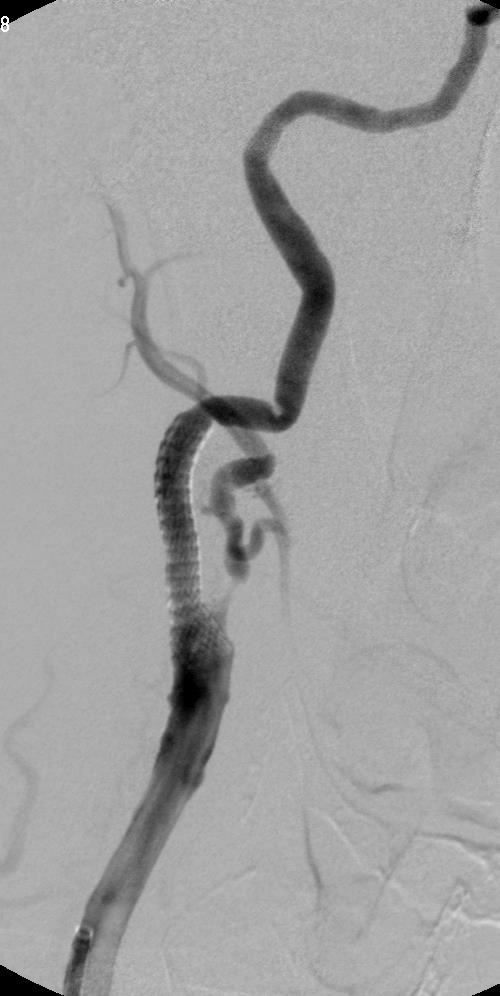
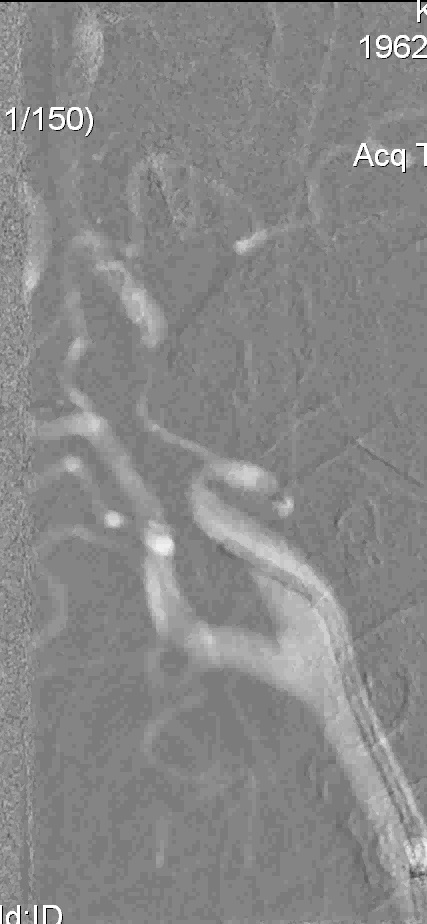
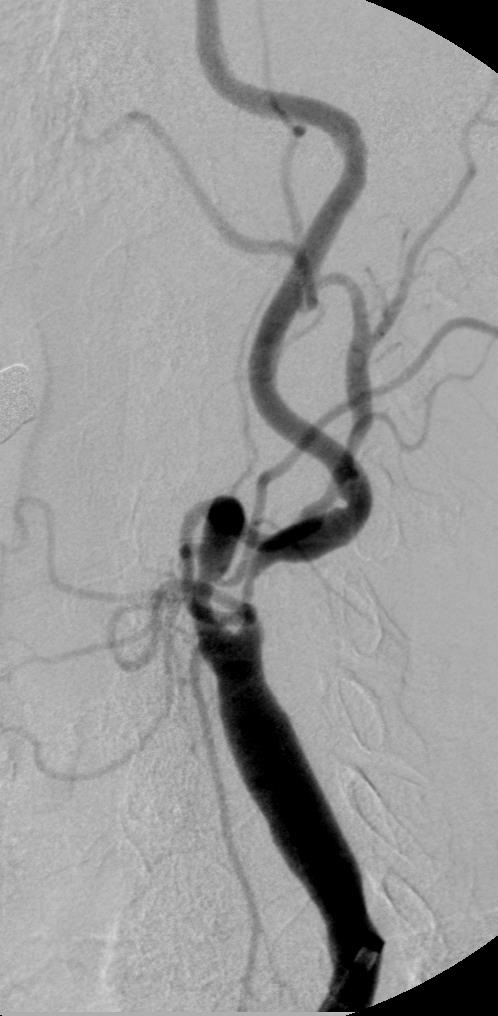
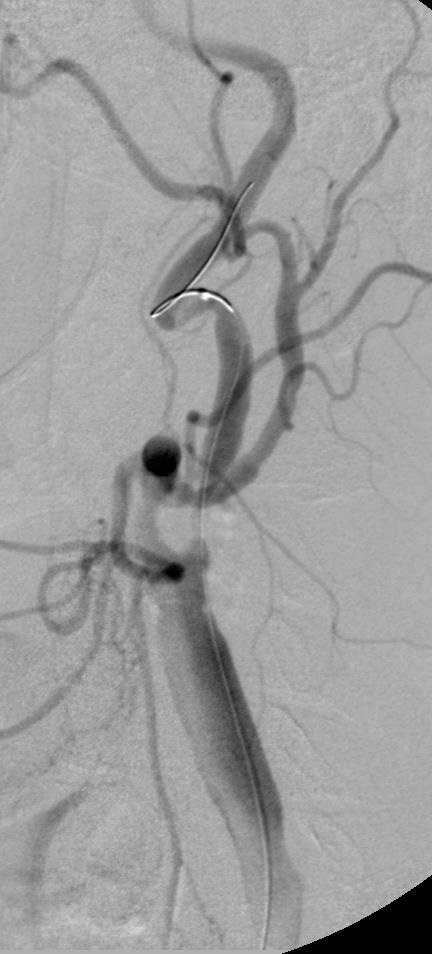
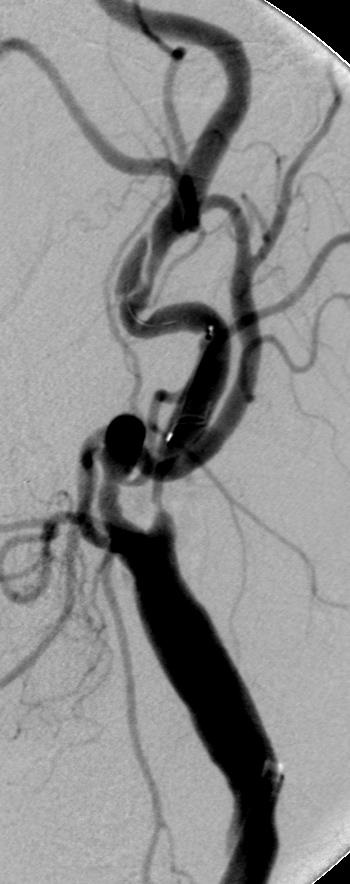
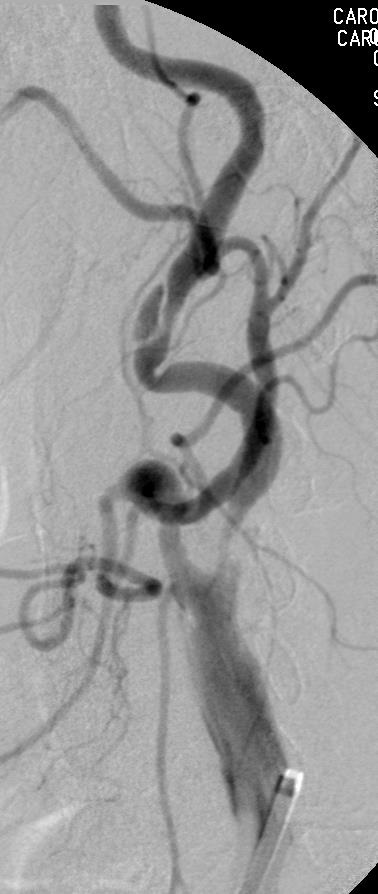
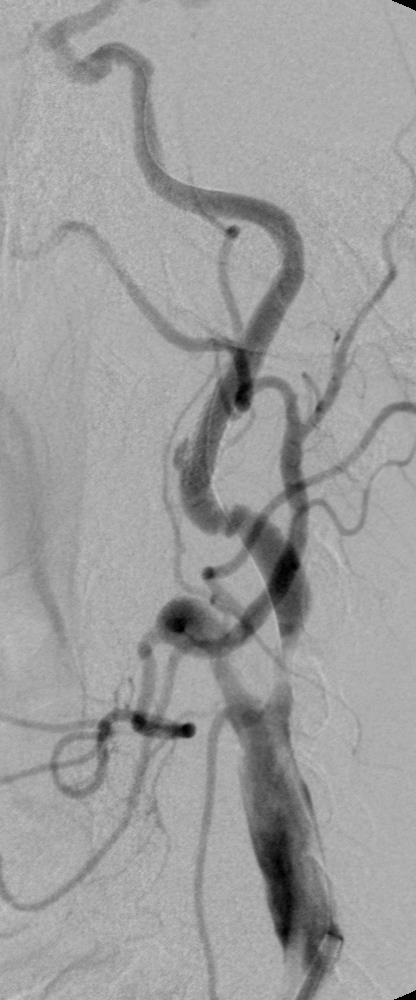
支撑架术围手术期的治疗(Peri-operative stenting treatment)
• 颈动脉支架后血小板激活和经常发生术后栓塞 Platelet activation and frequent post-op emboli following carotid stenting
轻度并发症1. 颈动脉痉挛 Carotid artery spasm
通常由EPD(embolic protection devices,)引起,自发缓解,如果持续性导致血流受限:硝酸甘油 100-300μg 动脉注射
2. 低血压/心动过缓 Sustained hypotension / bradycardia1)暂时性心动过缓和低血压 Transient bradycardia and hypotension
• 颈动脉分叉扩张的生理性反应 Physiological response to dilatation of carotid bifurcation.
• 治疗前0.5mg-1mg 阿托品 Pre-treatment with 0.5mg-1mg atropine.
• 颈动脉支架后12小时脱离监护 Close monitor 12h post CAS.
– 心脏疾病 Cardiac pathologies
– 血管入路部位出血 Bleeding from the site of vascular access.
2)严重持续性低血压
3. 颈动脉夹层 Carotid artery dissection
• 颈内动脉严重迂曲或扭结 Severe "bends" or "kinks" in the ICA.
• 颈动脉内过度操作相关,包括导丝、球囊导管和支架 Aggressive hardware (guide wires, balloon catheters, stents) within the ICA.
• 颈内动脉支架远端后扩张 Postdilatation of the distal stent edge within the ICA.
• 颈总动脉内导管鞘头端过度操作 Aggressive manipulation of the guiding sheath tip, in the common carotid artery.
4. 造影剂脑病(非常罕见)Contrast encephalopathy (very rare)
5. 轻度暂短性脑缺血发作 Minor embolic neurological events (TIAs)
• 来自介入治疗时从病变脱落的碎渣 Debris from the site of the lesion during the intervention
• 患者神经状态发生明显变化 Significant change in the patient’s neurological status.
• 维持血压/心率/气道 Maintain blood pressure/ heart rate/ viable airway.
• 如果患者发生不合作和极度躁动:呼叫麻醉科医生 If the patient becomes uncooperative and agitated: anesthesiologist!
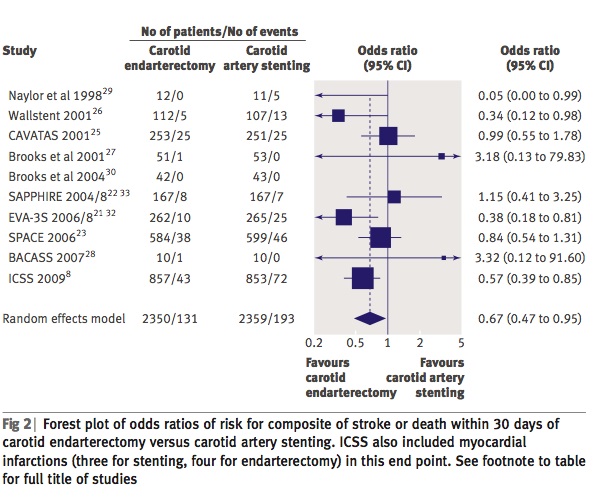
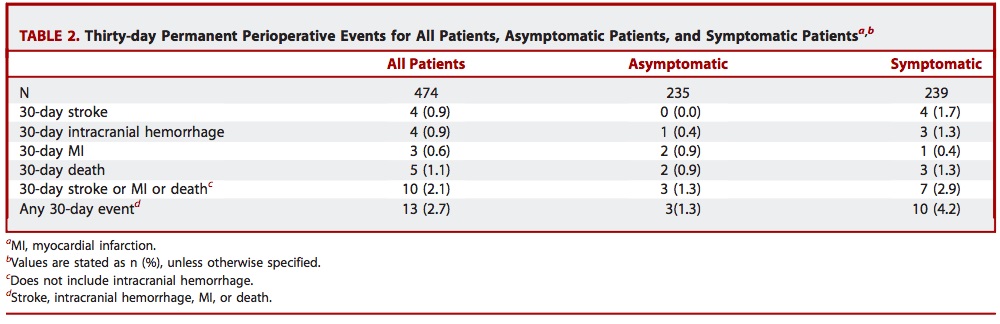
CREST试验 [标准风险患者]:4年间 CAS和CEA之间主要终点事件的无显著差异
1. 卒中
2. 心肌梗死(MI) 3. 死亡 4. 同侧卒中 尽管使用CAS的中风的风险更高,CEA发生心肌梗死的风险较高(但无显著差异)。 CREST trial [standard risk patients]: no significant differences between CAS and CEA for the primary endpoint: periprocedural
stroke, myocardial infarction (MI), or death and ipsilateral stroke up to four years although a higher risk of stroke with CAS and
a higher risk of MI with CEA were observed.
Brott TG, et al. Stenting versus endarterectomy for treatment of carotid-artery stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2010
  Risk factors for periprocedural distal embolization during CAS are the following:
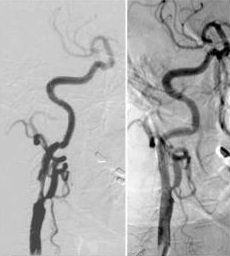
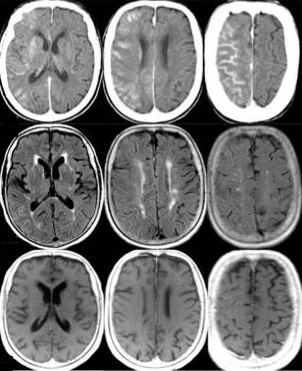
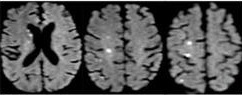
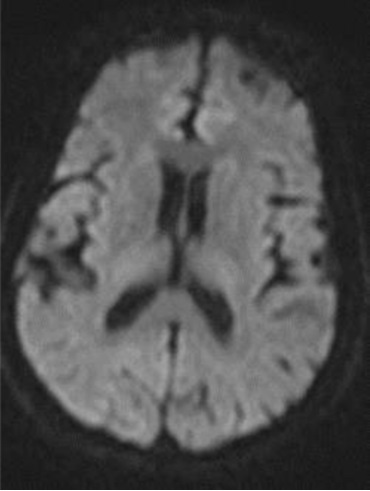
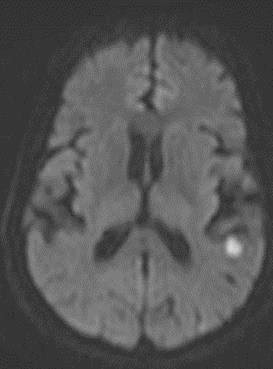
脑梗死 Brain embolization:
• 颈动脉支架后需要前后位颅内动脉判断是否有脑梗死,需要与颈动脉支架前的DSA比较。DSAIntracranial DSA in AP and lateral projections. Compare with pre CAS angio.
• 颅内栓塞最可能的位置是大脑中动脉分支和颈内动脉远端 The most likely sites of intracranial embolism are the distal ICA and the middle cerebral artery branches.
• 没有术前颅内DSA不做颈动脉支架 DO dot perform CAS without pre op intracranial DSA!
脑梗死?时间就是大脑! 大血管栓塞:试图尽可能快的再通阻塞的分支(机械的血栓取出或溶栓剂) 6. 血管入路并发症 Complications at the site of the vascular access重度并发症
1. 严重栓塞性中风 Major embolic stroke
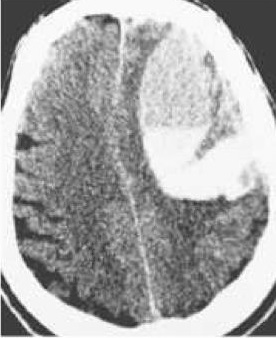
2. 颅内出血 Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH)
突然头痛或失去意识,立即终止操作,用鱼精蛋白中和肝素,即刻进行脑CT检查
• 颈动脉支架严重并发症通常危及生命 life-threatening and usually fatal.
• 发生率 0.3% of CAS.
• 过度抗凝、高血压控制不良、积极尝试颅内神经血管抢救,特别是脆弱的浆果动脉瘤。combination of excessive anticoagulation, poorly controlled hypertension, aggressive attempts at intracranial neurovascular rescue, presence of a vulnerable berry aneurysm.
• 最近(<三周 )发生缺血性中风的颈动脉支架CAS in the presence of a recent (<3 weeks previously) ischemic stroke.
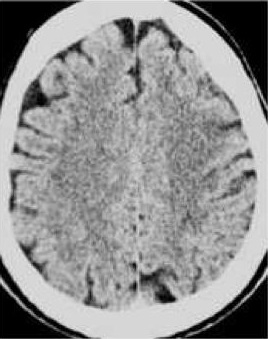
3. 高灌注综合征 Hyperperfusion syndrome
脑过度灌注综合症(cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome, CHS)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
The mechanism is related to long-standing hypoperfusion that results in impaired autoregulation of the microcirculation
高灌注综合征处理 Hyperperfusion syndrome: management
4. 颈动脉破裂非常罕见 Carotid perforation (very rare)
5. 急性支架血栓形成非常罕见 Acute stent thrombosis (very rare)
• 支架大小合适以及支架贴壁 Proper stent sizing and careful stent opposition to the arterial wall.
颈动脉支架并发症危险因素 CAS: Increased risk for complications
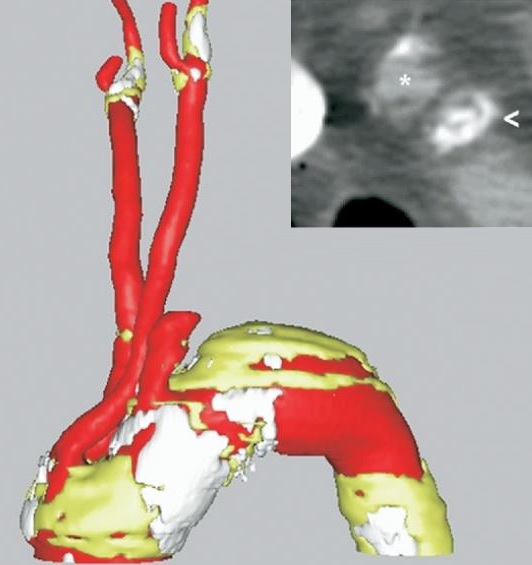 |
| 颈动脉与主动脉弓成角 Significant atherosclerosis and angulation of the aortic arch. |
 |
 |
In conclusion
- 颈动脉支架相对于颈动脉内膜剥脱术是一个选项 CAS is an alternative procedure for CEA.
- 有经验的医生并发症发生率比最好的颈动脉内膜剥脱术最好的结果低 If used by experienced doctor the complication rate is low-comparable with best CEA results.
- 阿喀琉斯之踵是围手术期的栓塞。虽然大多数是亚临床的。 必须全面了解并发症的知识,对于预防,避免和治疗是必需的。The Achilles tendon is the periprocedural embolization –although mostly subclinical.Thorough knowledge of the omplications is mandatory to prevent, avoid and treat.